Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Graphs and Coordinates
Problem 77
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 75–78, list the quadrant or quadrants satisfying each condition. x^3 > 0 and y^3 <0
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadrants of the Cartesian Plane
The Cartesian plane is divided into four quadrants based on the signs of the x and y coordinates. Quadrant I has positive x and y values, Quadrant II has negative x and positive y values, Quadrant III has negative x and y values, and Quadrant IV has positive x and negative y values. Understanding these quadrants is essential for determining where specific inequalities hold true.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
Inequalities and Their Solutions
Inequalities express a relationship where one side is not equal to the other, often involving greater than (>) or less than (<) symbols. In this case, x^3 > 0 indicates that x must be positive, while y^3 < 0 indicates that y must be negative. Solving these inequalities helps identify the regions in the Cartesian plane that satisfy the given conditions.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Cubic Functions and Their Behavior
Cubic functions, such as f(x) = x^3, have specific characteristics based on the sign of x. For positive x, the output is positive, and for negative x, the output is negative. This behavior is crucial for interpreting the inequalities x^3 > 0 and y^3 < 0, as it directly informs us about the possible values of x and y in the context of the quadrants.
Recommended video:
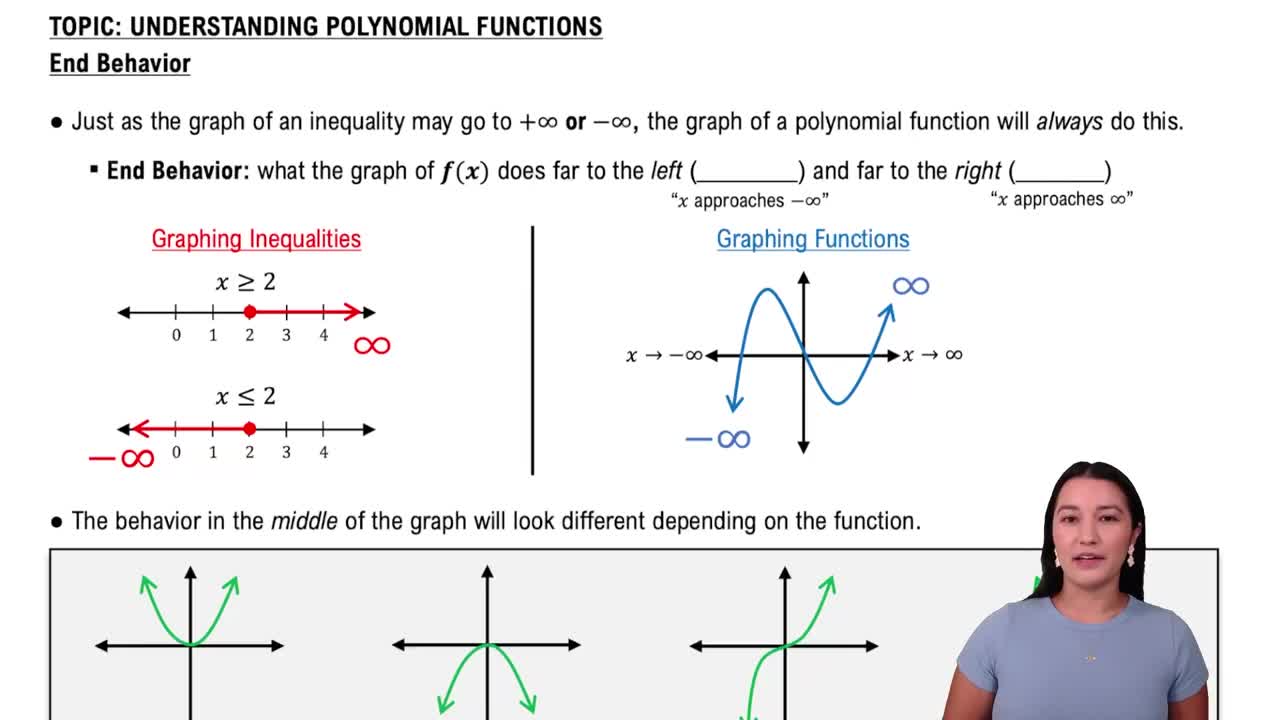
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions

 5:10m
5:10mWatch next
Master Graphs & the Rectangular Coordinate System with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice