Graph each rational function. See Examples 5–9. ƒ(x)=[(x-5)(x-2)]/(x^2+9)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Graphing Rational Functions
Problem 35Lial - 13th Edition
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionMatch the rational function in Column I with the appropriate descrip-tion in Column II. Choices in Column II can be used only once. ƒ(x)=(x^2+3x+4)/(x-5)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the quotient of two polynomials. In the given function ƒ(x)=(x^2+3x+4)/(x-5), the numerator is a polynomial of degree 2, and the denominator is a polynomial of degree 1. Understanding the structure of rational functions is essential for analyzing their behavior, including asymptotes and intercepts.
Recommended video:
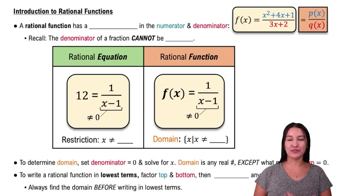
Intro to Rational Functions
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For rational functions, the domain excludes any values that make the denominator zero. In this case, the function ƒ(x) is undefined when x=5, so the domain is all real numbers except x=5.
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes
Asymptotes are lines that the graph of a function approaches but never touches. Vertical asymptotes occur where the function is undefined, typically at values that make the denominator zero, such as x=5 for this function. Horizontal asymptotes describe the behavior of the function as x approaches infinity or negative infinity, which can be determined by comparing the degrees of the numerator and denominator.
Recommended video:

Determining Horizontal Asymptotes

 5:31m
5:31mWatch next
Master Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
22
views
Graphing Rational Functions practice set


