Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. In the case of h(x) = (x + 7) / (x^2 - 49), the numerator is a linear polynomial and the denominator is a quadratic polynomial. Understanding the structure of rational functions is essential for analyzing their properties, including their domain.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rational Functions
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For rational functions, the domain is restricted by the values that make the denominator zero, as division by zero is undefined. Identifying these restrictions is crucial for determining the domain of h(x).
Recommended video:
Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Finding Restrictions
To find the domain of a rational function, one must identify the values of x that cause the denominator to equal zero. For h(x), this involves solving the equation x^2 - 49 = 0, which factors to (x - 7)(x + 7) = 0. The solutions, x = 7 and x = -7, indicate the points where the function is undefined, thus defining the domain.
Recommended video:
Restrictions on Rational Equations
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution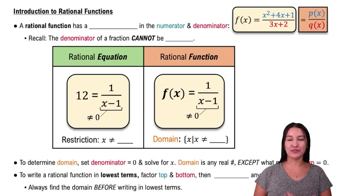



 6:24m
6:24m