Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
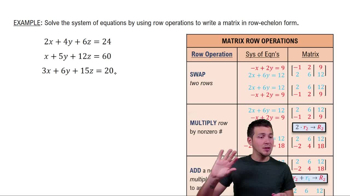
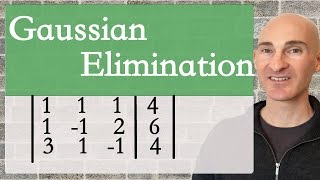
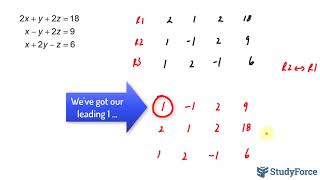
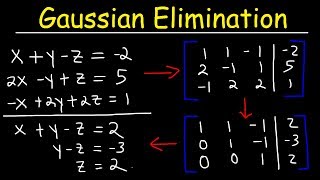
Introduction to Matrices
Problem 43d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 43–46, perform each long division and write the partial fraction decomposition of the remainder term. (x^5+2)/(x^2-1)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
10mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Long Division of Polynomials
Long division of polynomials is a method used to divide a polynomial by another polynomial of lower degree. It involves dividing the leading term of the dividend by the leading term of the divisor, multiplying the entire divisor by this result, and subtracting it from the dividend. This process is repeated until the degree of the remainder is less than the degree of the divisor.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Polynomials
Partial Fraction Decomposition
Partial fraction decomposition is a technique used to express a rational function as a sum of simpler fractions. This is particularly useful when integrating rational functions. The process involves factoring the denominator and expressing the function as a sum of fractions whose denominators are the factors of the original denominator, allowing for easier manipulation and integration.
Recommended video:

Decomposition of Functions
Remainder Theorem
The Remainder Theorem states that when a polynomial f(x) is divided by a linear divisor of the form (x - c), the remainder of this division is f(c). In the context of polynomial long division, the remainder can be expressed as a polynomial of lower degree than the divisor, which is essential for performing partial fraction decomposition and understanding the overall division process.
Recommended video:

Higher Powers of i

 4:35m
4:35mWatch next
Master Introduction to Matrices with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice