Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Graphing Rational Functions
Problem 66a
Textbook Question
Graph each rational function. See Examples 5–9. ƒ(x)=(6-3x)/(4-x)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
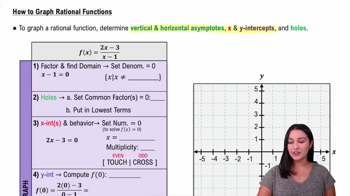
Identify the vertical asymptote by setting the denominator equal to zero and solving for x: \(4 - x = 0\).
Determine the horizontal asymptote by comparing the degrees of the numerator and the denominator. Since both are linear (degree 1), divide the leading coefficients: \(-\frac{3}{-1}\).
Find the x-intercept by setting the numerator equal to zero and solving for x: \(6 - 3x = 0\).
Find the y-intercept by evaluating \(f(0)\).
Plot the asymptotes, intercepts, and sketch the graph, considering the behavior of the function as it approaches the asymptotes.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
9mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. The general form is f(x) = P(x)/Q(x), where P and Q are polynomials. Understanding rational functions involves analyzing their behavior, including asymptotes, intercepts, and domain restrictions, which are crucial for graphing them accurately.
Recommended video:
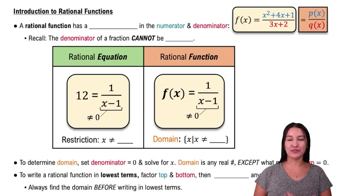
Intro to Rational Functions
Asymptotes
Asymptotes are lines that a graph approaches but never touches. There are vertical asymptotes, which occur where the denominator of a rational function equals zero, and horizontal asymptotes, which describe the behavior of the function as x approaches infinity. Identifying these asymptotes is essential for understanding the overall shape of the graph.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Asymptotes
Intercepts
Intercepts are points where the graph of a function crosses the axes. The x-intercept occurs when f(x) = 0, which is found by setting the numerator of the rational function to zero. The y-intercept is found by evaluating the function at x = 0. Knowing the intercepts helps in sketching the graph and understanding the function's behavior.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphing Intercepts

 5:31m
5:31mWatch next
Master Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice