Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 60
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionShow that the real zeros of each polynomial function satisfy the given conditions. See Example 6. ƒ(x)=x^5+2x^3-2x^2+5x+5; no real zero less than -1
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
7mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
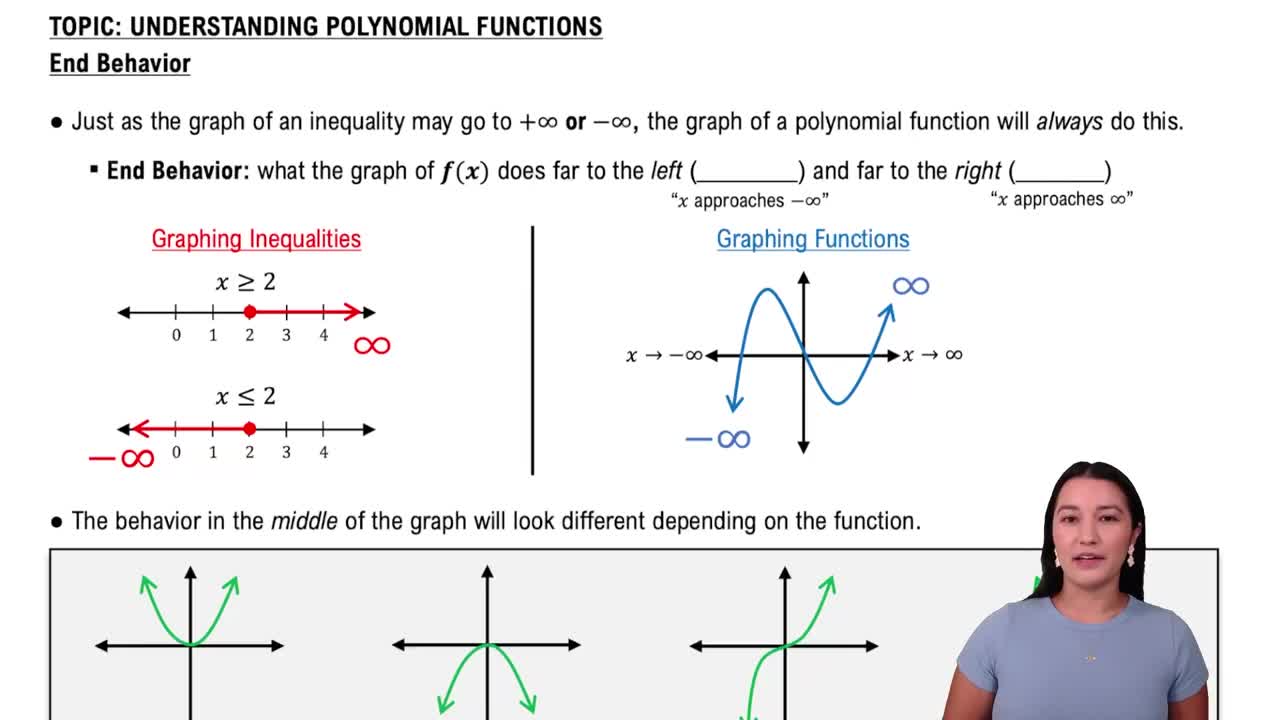
Polynomial Functions
A polynomial function is a mathematical expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients. The general form is f(x) = a_n*x^n + a_(n-1)*x^(n-1) + ... + a_1*x + a_0, where 'n' is a non-negative integer and 'a_n' is not zero. Understanding the behavior of polynomial functions, including their degree and leading coefficient, is essential for analyzing their zeros.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Real Zeros
Real zeros of a polynomial function are the values of 'x' for which the function evaluates to zero. These zeros can be found using various methods, including factoring, the Rational Root Theorem, or numerical methods. Identifying the real zeros is crucial for understanding the function's graph and its intersections with the x-axis.
Recommended video:

Finding Zeros & Their Multiplicity
Inequalities and Interval Testing
Inequalities and interval testing involve determining the sign of a polynomial function over specific intervals. By evaluating the function at test points within these intervals, one can ascertain where the function is positive or negative. This technique is particularly useful for establishing conditions such as the absence of real zeros in certain ranges, as required in the given problem.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice