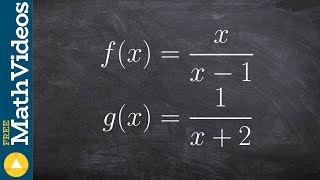Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Function Composition
Problem 125
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionExercises 123–125 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Solve for y: x = y² -1, y ≥ 0.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants and a ≠ 0. In the context of the given question, the equation x = y² - 1 can be rearranged to form a standard quadratic equation in terms of y, allowing for the application of methods such as factoring or the quadratic formula to find the values of y.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Quadratic Equations
Square Roots
Square roots are the values that, when multiplied by themselves, yield the original number. In solving the equation x = y² - 1, isolating y² leads to y = √(x + 1). Understanding how to manipulate square roots is essential, especially since the problem specifies y ≥ 0, indicating that only the non-negative root is relevant.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Domain and Range
The domain refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for a function, while the range refers to the set of possible output values (y-values). In this problem, the condition y ≥ 0 restricts the range of the solution, which is crucial for determining valid solutions to the equation and understanding the behavior of the function represented by the equation.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions

 4:56m
4:56mWatch next
Master Function Composition with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice