Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Quadratic Formula
Problem 96a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionAnswer each question. Find the values of a, b, and c for which the quadratic equation. ax^2 + bx + c = 0 has the given numbers as solutions. (Hint: Use the zero-factor property in reverse.) -3, 2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. The solutions to this equation, known as the roots, can be found using various methods, including factoring, completing the square, or applying the quadratic formula. Understanding the structure of quadratic equations is essential for solving them.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Quadratic Equations
Zero-Product Property
The zero-product property states that if the product of two factors equals zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero. This principle is crucial when solving quadratic equations by factoring, as it allows us to set each factor equal to zero to find the solutions. In this context, it helps in determining the values of a, b, and c when given the roots.
Recommended video:

Product, Quotient, and Power Rules of Logs
Factoring Quadratics
Factoring quadratics involves expressing the quadratic equation in the form (x - r1)(x - r2) = 0, where r1 and r2 are the roots of the equation. This method simplifies finding the coefficients a, b, and c by relating them to the roots. For the given roots -3 and 2, the factored form would be (x + 3)(x - 2), leading to the identification of the coefficients.
Recommended video:
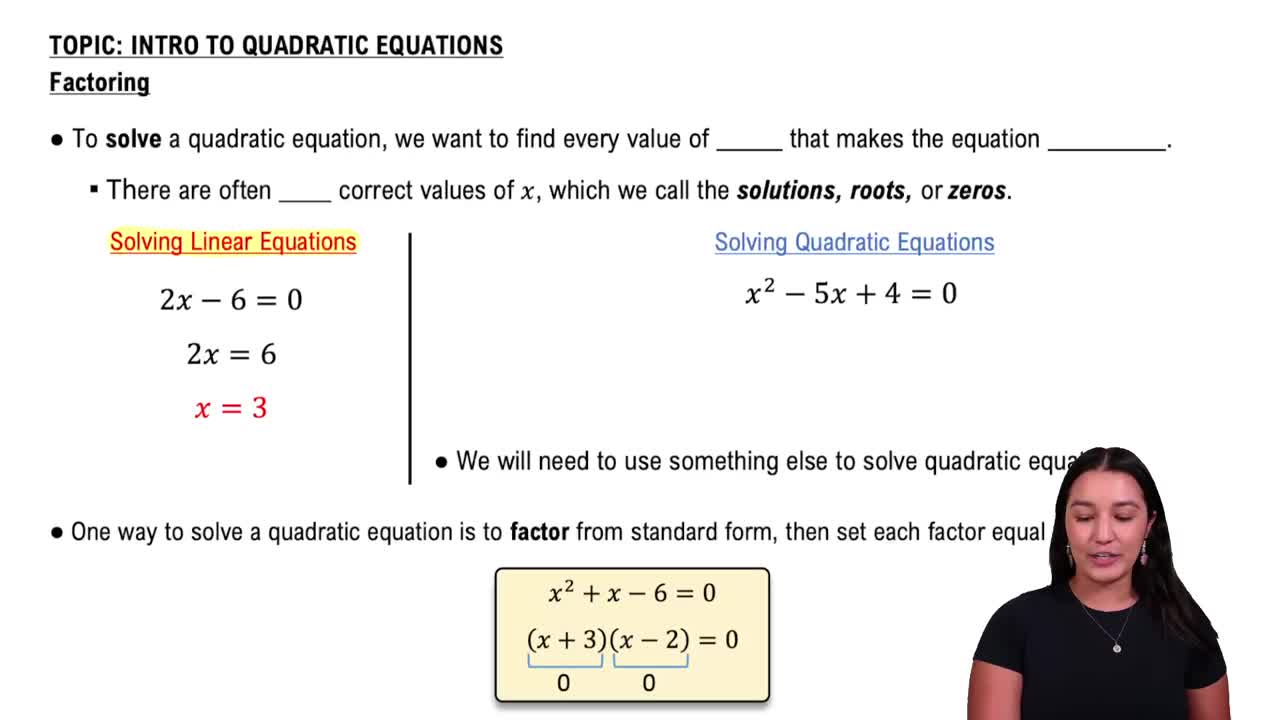
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring

 6:36m
6:36mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice







