Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Inequalities
Problem 17d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSolve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. See Example 1. x^2 + x - 30 ≤ 0
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Inequalities
Quadratic inequalities are expressions that involve a quadratic polynomial set in relation to a value, typically using symbols like ≤, ≥, <, or >. To solve these inequalities, one must find the values of the variable that satisfy the inequality, often by determining the roots of the corresponding quadratic equation and analyzing the sign of the quadratic expression in the intervals defined by these roots.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Nonlinear Inequalities
Interval Notation
Interval notation is a mathematical notation used to represent a range of values. It uses parentheses and brackets to indicate whether endpoints are included (closed interval) or excluded (open interval). For example, the interval [a, b] includes both a and b, while (a, b) does not include them. This notation is essential for expressing the solution set of inequalities succinctly.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Factoring Quadratics
Factoring quadratics involves rewriting a quadratic expression as a product of its linear factors. This process is crucial for solving quadratic inequalities, as it allows one to identify the roots of the equation, which are the points where the expression equals zero. For example, the quadratic x^2 + x - 30 can be factored into (x - 5)(x + 6), making it easier to analyze the sign of the expression across different intervals.
Recommended video:
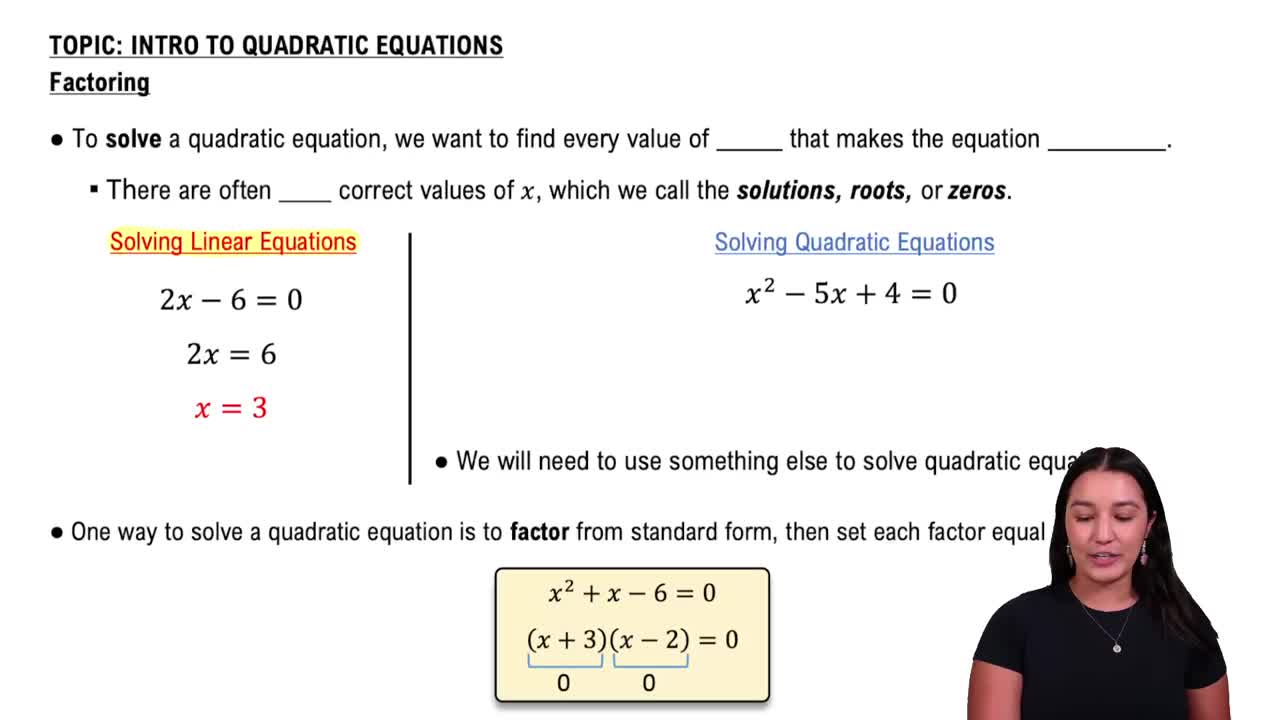
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
Related Videos
Related Practice