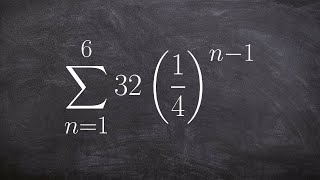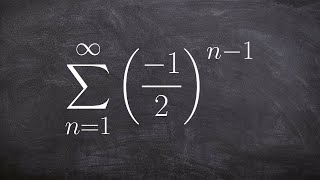Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
9. Sequences, Series, & Induction
Geometric Sequences
Problem 37b
Textbook Question
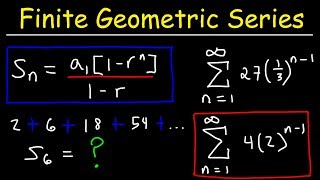
Textbook QuestionUse the formula for the general term (the nth term) of a geometric sequence to find the indicated term of the sequence. Find a(sub 5) when a(sub 1) = -3, r = 2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Geometric Sequence
A geometric sequence is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. This type of sequence can be expressed in the form a(n) = a(1) * r^(n-1), where a(n) is the nth term, a(1) is the first term, r is the common ratio, and n is the term number.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Geometric Sequences - Recursive Formula
General Term Formula
The general term formula for a geometric sequence allows us to calculate any term in the sequence based on its position. Specifically, the nth term can be calculated using the formula a(n) = a(1) * r^(n-1). This formula is essential for finding specific terms in the sequence, such as a(sub 5) in this case.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Writing a General Formula
Common Ratio
The common ratio in a geometric sequence is the factor by which we multiply each term to get the next term. It is denoted by 'r' and is crucial for determining the growth or decay of the sequence. In the given problem, the common ratio is 2, meaning each term is double the previous term, which directly influences the calculation of a(sub 5).
Recommended video:

Graphs of Common Functions

 4:18m
4:18mWatch next
Master Geometric Sequences - Recursive Formula with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice