Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
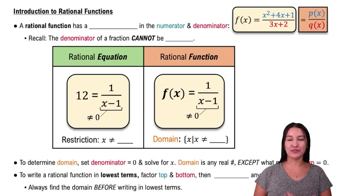
Introduction to Rational Functions
Problem 1
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionProvide a short answer to each question. What is the domain of the function ƒ(x)=1/x? What is its range?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For the function ƒ(x) = 1/x, the domain excludes any value that would make the denominator zero, which in this case is x = 0. Therefore, the domain is all real numbers except zero, often expressed as (-∞, 0) ∪ (0, ∞).
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Range of a Function
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values (y-values) that the function can produce. For ƒ(x) = 1/x, as x approaches zero from either side, the function values approach positive or negative infinity, but never actually reach zero. Thus, the range is also all real numbers except zero, represented as (-∞, 0) ∪ (0, ∞).
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Asymptotes
Asymptotes are lines that a graph approaches but never touches or crosses. In the case of the function ƒ(x) = 1/x, there is a vertical asymptote at x = 0, indicating that the function is undefined at this point. Additionally, there is a horizontal asymptote at y = 0, which shows that as x approaches infinity or negative infinity, the function values approach zero but never reach it.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Asymptotes

 6:4m
6:4mWatch next
Master Intro to Rational Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning