Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 40b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionGraph each polynomial function. Factor first if the polynomial is not in factored form. See Examples 3 and 4. ƒ(x)=-3x^4-5x^3+2x^2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
8mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Functions
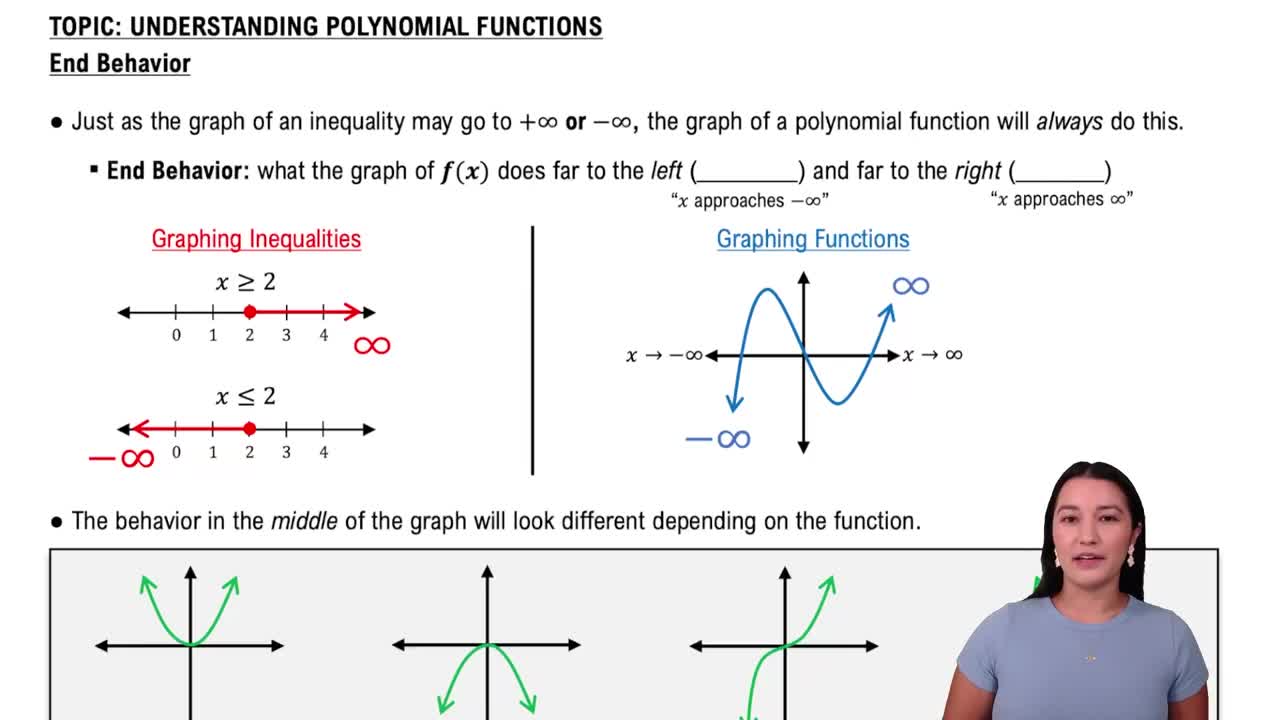
A polynomial function is a mathematical expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients. The general form of a polynomial in one variable is f(x) = a_n*x^n + a_(n-1)*x^(n-1) + ... + a_1*x + a_0, where 'n' is a non-negative integer and 'a_n' are constants. Understanding the degree and leading coefficient of the polynomial is crucial for graphing and analyzing its behavior.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Factoring Polynomials
Factoring polynomials involves rewriting the polynomial as a product of simpler polynomials or factors. This process can simplify the function and make it easier to find its roots, which are the x-values where the function equals zero. Common methods of factoring include taking out the greatest common factor, using the difference of squares, and applying the quadratic formula for second-degree polynomials.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Factoring Polynomials
Graphing Techniques
Graphing polynomial functions requires understanding their key features, such as intercepts, end behavior, and turning points. The x-intercepts can be found by setting the polynomial equal to zero and solving for x, while the y-intercept is found by evaluating the function at x=0. Analyzing the degree of the polynomial helps predict the number of turning points and the overall shape of the graph.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice