Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 103b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 79–112, use rational exponents to simplify each expression. If rational exponents appear after simplifying, write the answer in radical notation. Assume that all variables represent positive numbers. __ ⁴√√x
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Exponents
Rational exponents are a way to express roots using fractional powers. For example, the expression x^(1/n) represents the n-th root of x. This notation allows for easier manipulation of expressions involving roots, as it can be combined with other exponent rules. Understanding how to convert between radical and rational exponent forms is essential for simplifying expressions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
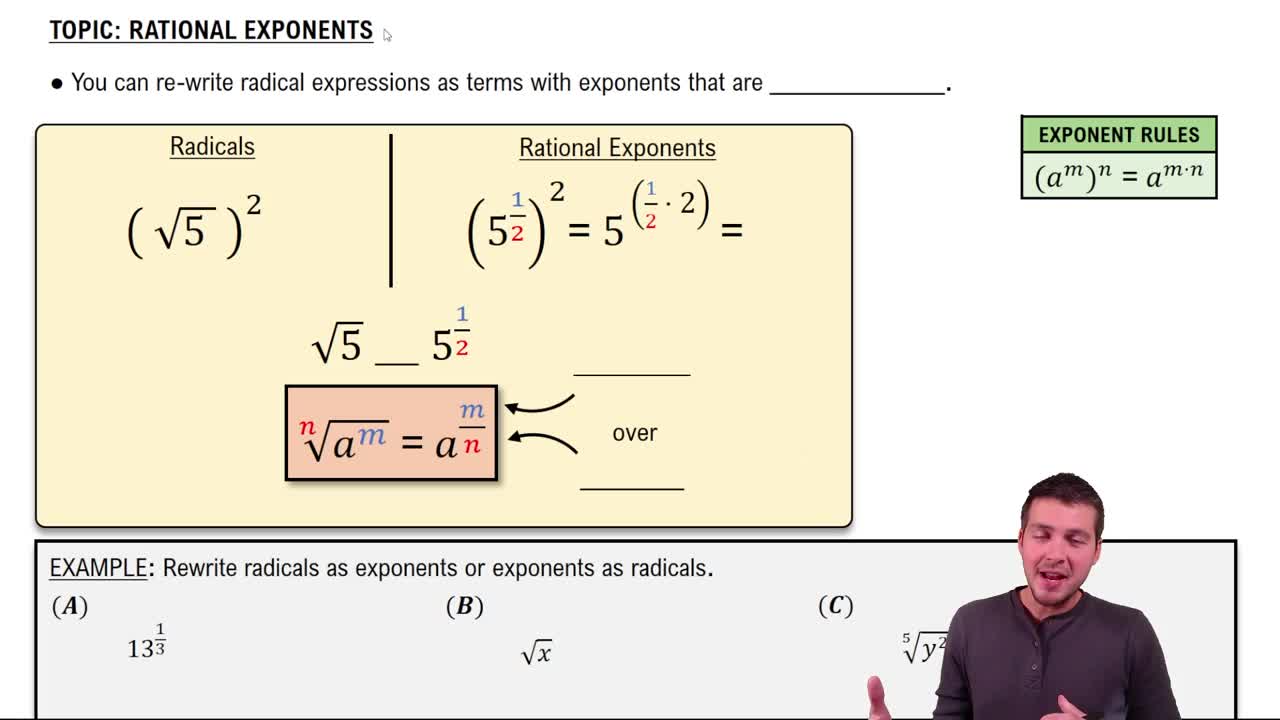
Rational Exponents
Radical Notation
Radical notation is a mathematical notation used to denote roots, such as square roots or cube roots. The radical symbol (√) indicates the root of a number, where the index of the root is specified if it is not a square root. For instance, √x represents the square root of x, while ⁴√x denotes the fourth root. Converting between radical and rational exponent forms is crucial for expressing simplified results.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Expanding Radicals
Simplifying Expressions
Simplifying expressions involves reducing them to their simplest form, making them easier to work with. This process often includes combining like terms, applying exponent rules, and converting between different forms of notation. In the context of rational exponents and radicals, simplification may require rewriting expressions to eliminate complex roots or fractional exponents, ensuring clarity and ease of interpretation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Related Videos
Related Practice