Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Long Division
Polynomial long division is a method used to divide a polynomial by another polynomial of lower degree. It involves a process similar to numerical long division, where you divide the leading term of the dividend by the leading term of the divisor, multiply the entire divisor by this result, and subtract it from the original polynomial. This process is repeated until the degree of the remainder is less than the degree of the divisor.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Polynomials
Leading Coefficient
The leading coefficient of a polynomial is the coefficient of the term with the highest degree. In the polynomial 4x^3 - 3x^2 - 2x + 1, the leading coefficient is 4. This value is crucial in long division as it determines how the first term of the quotient is calculated, influencing the subsequent steps of the division process.
Recommended video:
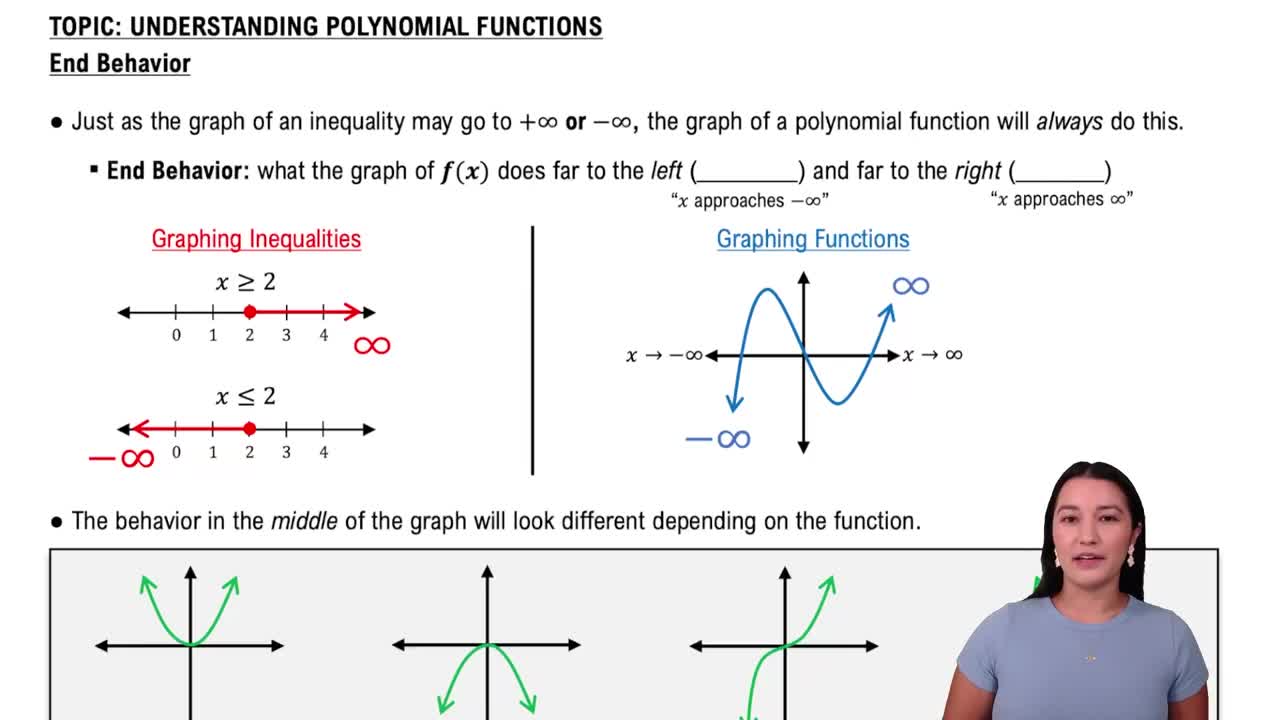
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions
Remainder Theorem
The Remainder Theorem states that when a polynomial f(x) is divided by a linear divisor of the form (x - c), the remainder of this division is equal to f(c). This theorem is useful for checking the results of polynomial long division, as it allows you to quickly verify the remainder by substituting the value of c into the original polynomial.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution