Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
Introduction to Logarithms
Problem 31a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 21–42, evaluate each expression without using a calculator. log2 (1/√2)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Logarithmic Functions
Logarithmic functions are the inverses of exponential functions. The logarithm log_b(a) answers the question: 'To what power must the base b be raised to obtain a?' Understanding this concept is crucial for evaluating logarithmic expressions, as it allows us to manipulate and simplify them effectively.
Recommended video:
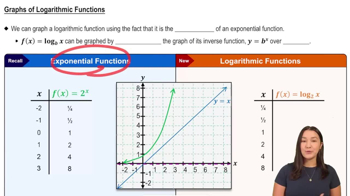
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Properties of Logarithms
Properties of logarithms, such as the product, quotient, and power rules, provide essential tools for simplifying logarithmic expressions. For instance, the property log_b(m/n) = log_b(m) - log_b(n) allows us to break down complex logarithmic expressions into simpler components, facilitating easier evaluation.
Recommended video:

Change of Base Property
Change of Base Formula
The change of base formula allows us to convert logarithms from one base to another, which can be particularly useful when dealing with logarithms of bases that are not easily computable. The formula states that log_b(a) = log_k(a) / log_k(b) for any positive k, enabling us to evaluate logarithms using more familiar bases.
Recommended video:

Change of Base Property

 7:3m
7:3mWatch next
Master Logarithms Introduction with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning




