Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponents and Radicals
Exponents represent repeated multiplication of a base number. For example, a number raised to a fractional exponent, such as 3/4, indicates both a root and a power: the denominator (4) signifies the root, while the numerator (3) indicates the power. Understanding how to manipulate these expressions is crucial for simplification.
Recommended video:
Negative Exponents
Negative exponents indicate the reciprocal of the base raised to the opposite positive exponent. For instance, x^(-n) equals 1/(x^n). In the context of this problem, simplifying expressions without negative exponents means rewriting any terms with negative exponents as positive fractions.
Recommended video:
Simplifying Expressions
Simplifying expressions involves reducing them to their simplest form, which often includes combining like terms, eliminating negative exponents, and applying the laws of exponents. This process is essential for clarity and ease of further calculations, especially when dealing with complex expressions.
Recommended video:
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution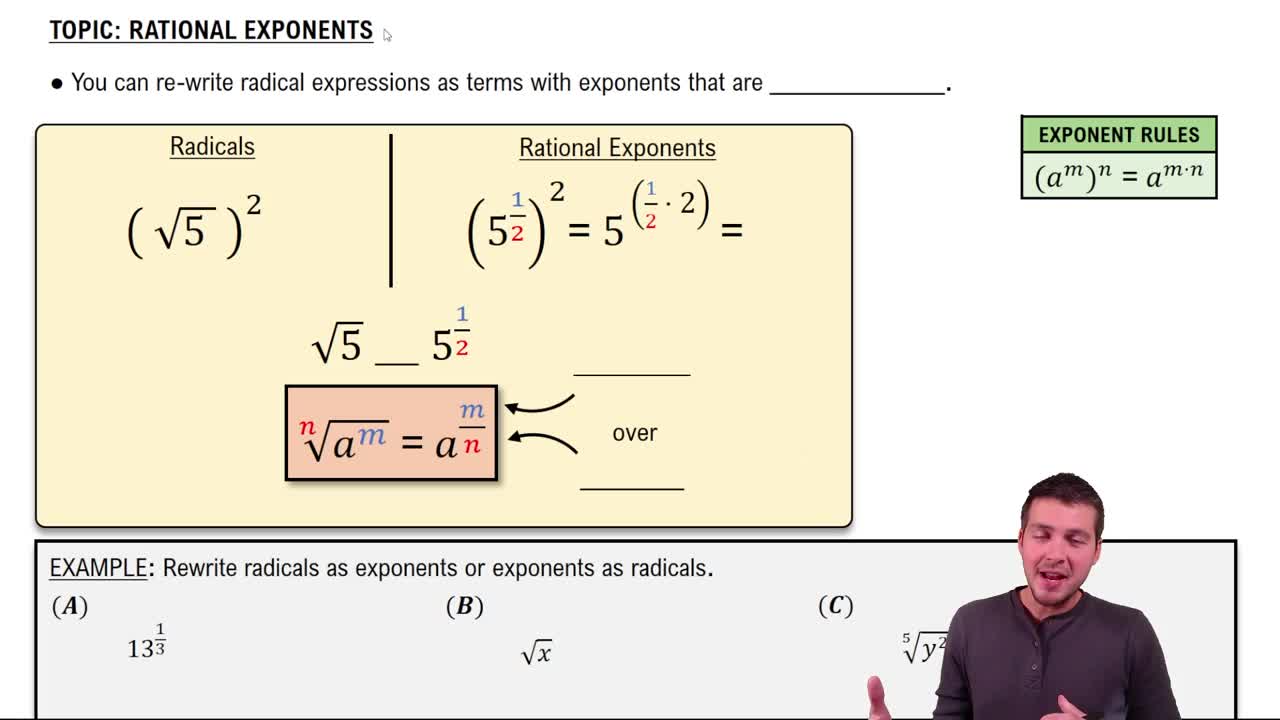



 4:06m
4:06m