Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 28c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–38, multiply as indicated. If possible, simplify any radical expressions that appear in the product. (√6 + √2) (√6 - √2)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Multiplying Binomials
Multiplying binomials involves applying the distributive property, often referred to as the FOIL method (First, Outside, Inside, Last). This technique helps in systematically multiplying each term in the first binomial by each term in the second binomial, ensuring that all combinations are accounted for. In the given expression, (√6 + √2)(√6 - √2), this method will yield a difference of squares.
Recommended video:
Guided course
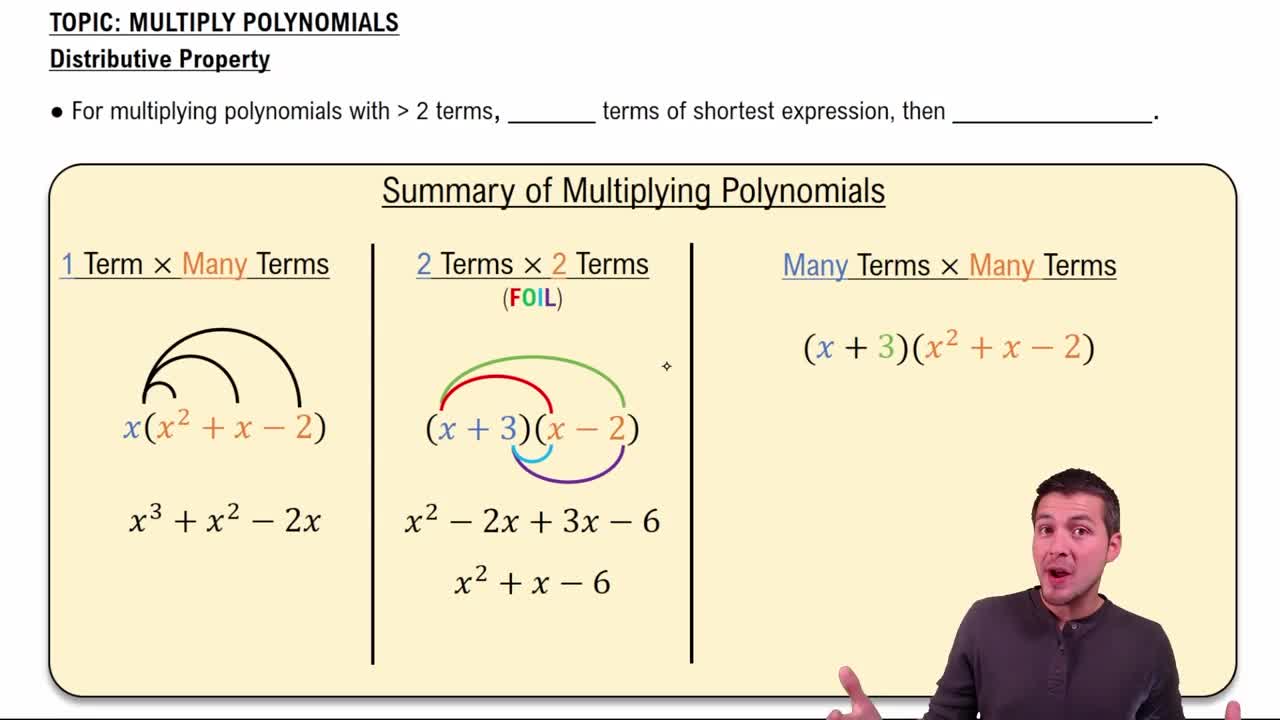
Multiply Polynomials Using the Distributive Property
Difference of Squares
The difference of squares is a specific algebraic identity that states a² - b² = (a + b)(a - b). This identity is particularly useful for simplifying expressions where one term is subtracted from another, both of which are perfect squares. In the context of the problem, recognizing that √6 and √2 are the 'a' and 'b' allows for a straightforward simplification of the product.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
Simplifying Radical Expressions
Simplifying radical expressions involves reducing the expression to its simplest form, which often includes combining like terms and removing any perfect squares from under the radical sign. This process is essential for clarity and ease of further calculations. In the given problem, after applying the difference of squares, any resulting radical expressions should be simplified to ensure the final answer is presented in its simplest form.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Radical Expressions with Fractions
Related Videos
Related Practice