Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Linear Equations
Problem 65a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn the metric system of weights and measures, temperature is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) instead of degrees Fahrenheit (°F). To convert between the two systems, we use the equations. C =5/9 (F-32) and F = 9/5C+32. In each exercise, convert to the other system. Round answers to the nearest tenth of a degree if necessary. 100°F
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Temperature Conversion
Temperature conversion involves changing a temperature value from one unit to another, such as from Fahrenheit to Celsius or vice versa. The formulas used for these conversions are derived from the linear relationship between the two scales, allowing for accurate transformations. Understanding how to apply these formulas is essential for solving problems related to temperature.
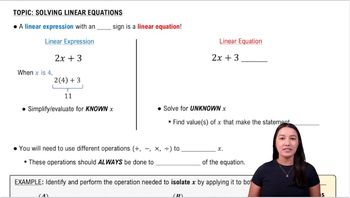
Linear Equations
The equations used for temperature conversion, C = 5/9 (F - 32) and F = 9/5C + 32, are examples of linear equations. These equations represent straight-line relationships between the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, where each unit change in one scale corresponds to a specific change in the other. Grasping the concept of linear equations is crucial for manipulating and solving these formulas.
Recommended video:

Categorizing Linear Equations
Rounding Numbers
Rounding numbers is the process of adjusting a numerical value to a specified degree of precision, often to simplify calculations or present results clearly. In the context of temperature conversion, rounding to the nearest tenth of a degree ensures that the final answer is both accurate and easy to interpret. Familiarity with rounding rules is important for presenting final results in a clear and concise manner.
Recommended video:

The Number e

 7:48m
7:48mWatch next
Master Introduction to Solving Linear Equtions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice