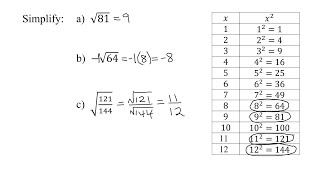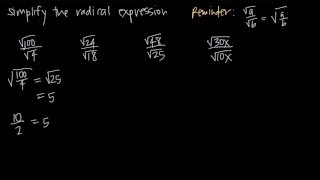Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
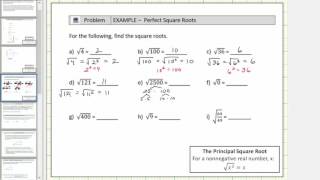
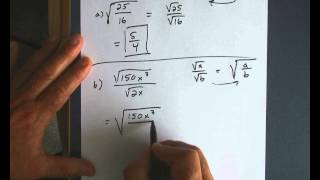
Radical Expressions
Problem 81b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionMatch each expression in Column I with its equivalent expression in Column II. See Example 8. a. (4/9)^3/2 b. (4/9)^-3/2 c. -(9/4)^3/2 d. -(9/4)^-3/2 A. 27/8 B. -27/8 C. 8/27 D. -8/27
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
13mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponents and Radicals
Exponents represent repeated multiplication of a base number, while radicals are the inverse operation, indicating the root of a number. Understanding how to manipulate expressions with fractional exponents is crucial, as they can represent both roots and powers. For example, an exponent of 1/2 indicates a square root, while a negative exponent signifies the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent.
Recommended video:
Guided course
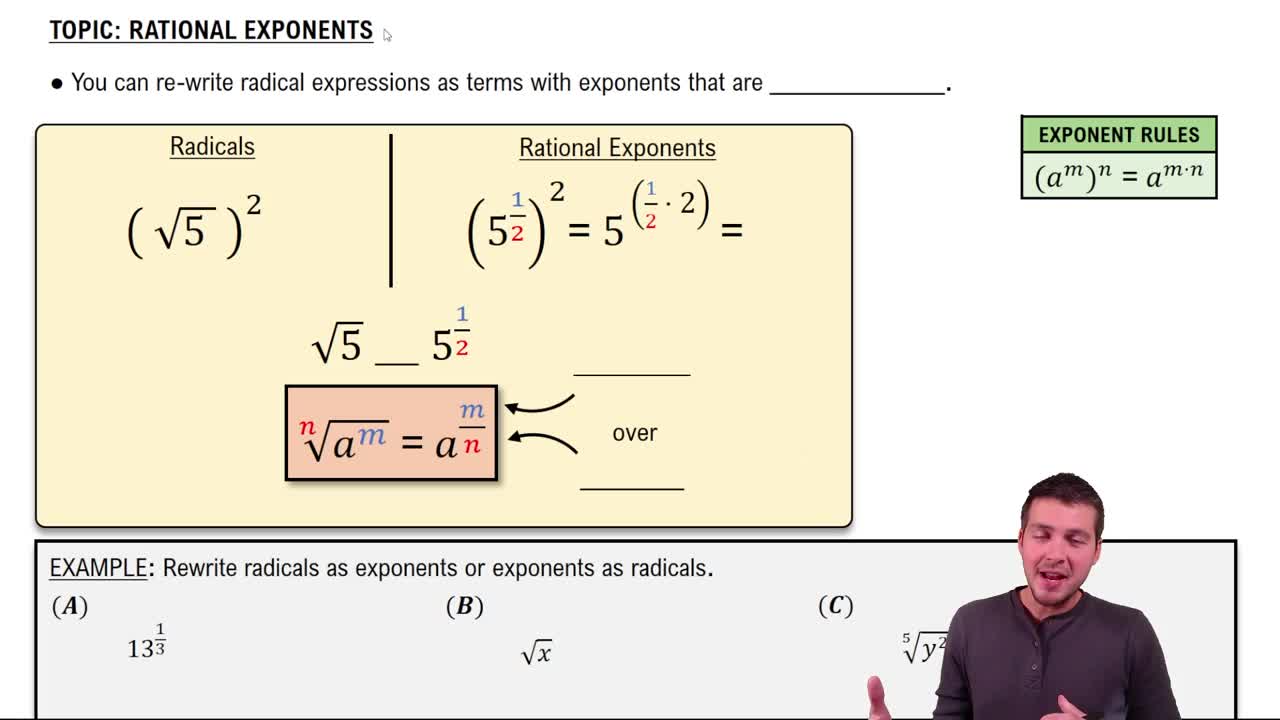
Rational Exponents
Negative Exponents
Negative exponents indicate that the base should be taken as the reciprocal. For instance, a term like (a^(-n)) can be rewritten as 1/(a^n). This concept is essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations, especially when dealing with negative fractional exponents, as it allows for easier manipulation of the terms involved.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Zero and Negative Rules
Simplifying Rational Expressions
Simplifying rational expressions involves reducing fractions to their simplest form by canceling common factors. This process is vital when working with expressions that contain exponents, as it helps in identifying equivalent forms. For example, when simplifying (4/9)^(3/2), one must calculate the square root and then raise the result to the third power, ensuring clarity in the final expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Related Videos
Related Practice