Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
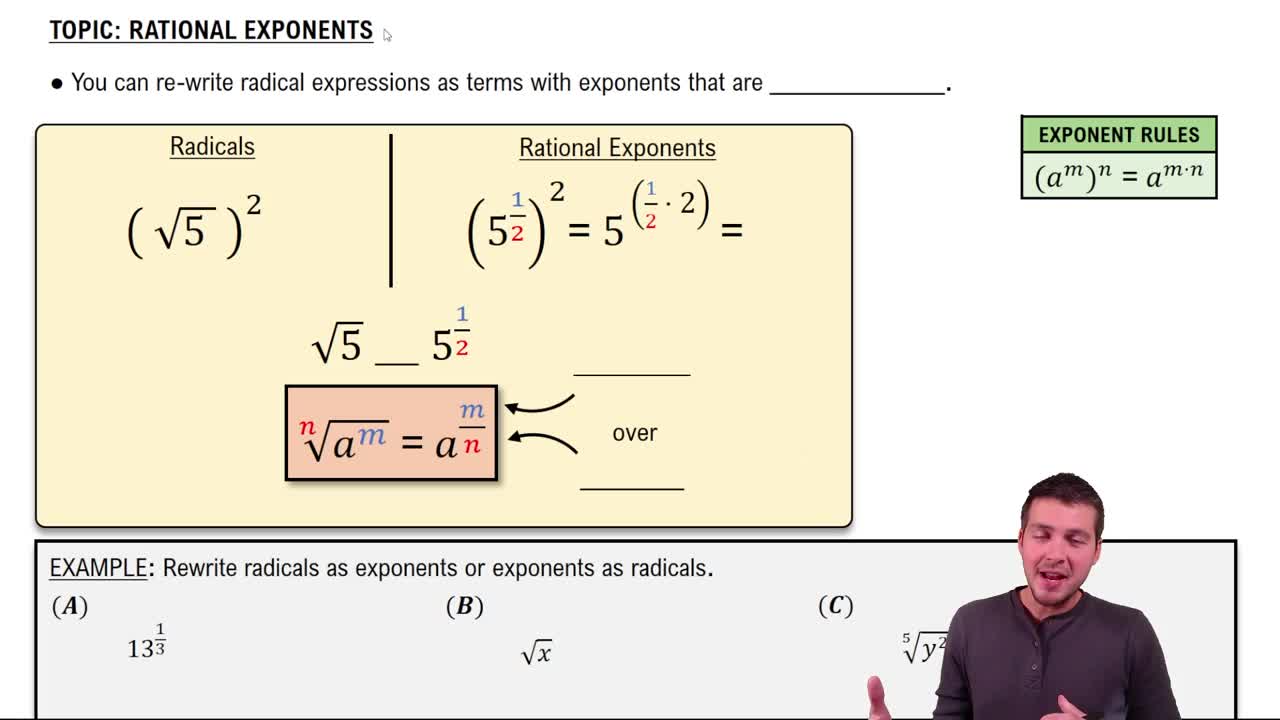
Rational Exponents
Rational exponents represent roots and powers in a compact form. For example, an exponent of 1/3 indicates the cube root of a number. This concept allows us to express operations involving roots using exponentiation, making calculations more straightforward.
Recommended video:
Negative Numbers and Roots
When dealing with negative numbers, the cube root can yield real results, unlike even roots. The cube root of a negative number is also negative, which is essential for evaluating expressions like (-64/27)^(1/3). Understanding how roots behave with negative values is crucial for accurate calculations.
Recommended video:
Square Roots of Negative Numbers
Fractional Bases
Evaluating expressions with fractional bases involves simplifying the fraction before applying the exponent. In this case, -64/27 can be simplified to its cube root by separately finding the cube roots of the numerator and denominator. This concept is vital for breaking down complex expressions into manageable parts.
Recommended video:
Radical Expressions with Fractions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution