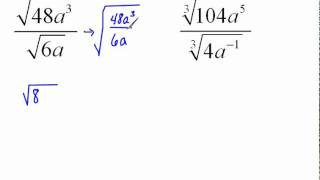Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 67c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 59–72, simplify each expression using the products-to-powers rule. (-3x⁻²)⁻³
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponents and Powers
Exponents represent repeated multiplication of a base number. The power indicates how many times the base is multiplied by itself. Understanding the laws of exponents, such as the product of powers and power of a power, is essential for simplifying expressions involving exponents.
Recommended video:

Powers of i
Negative Exponents
A negative exponent indicates the reciprocal of the base raised to the opposite positive exponent. For example, x⁻ⁿ = 1/xⁿ. This concept is crucial when simplifying expressions with negative exponents, as it allows for rewriting them in a more manageable form.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Zero and Negative Rules
Products-to-Powers Rule
The products-to-powers rule states that when raising a product to a power, you can distribute the exponent to each factor in the product. For instance, (ab)ⁿ = aⁿbⁿ. This rule is vital for simplifying expressions like (-3x⁻²)⁻³, as it allows for the individual simplification of each component.
Recommended video:

Product, Quotient, and Power Rules of Logs
Related Videos
Related Practice