Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 10b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 10–13, use the Leading Coefficient Test to determine the end behavior of the graph of the given polynomial function. Then use this end behavior to match the polynomial function with its graph. [The graphs are labeled (a) through (d).] f(x) = -x^3 + x^2 + 2x
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Leading Coefficient Test
The Leading Coefficient Test is a method used to determine the end behavior of polynomial functions based on the sign and degree of the leading term. For a polynomial of the form f(x) = ax^n, where 'a' is the leading coefficient and 'n' is the degree, the test states that if 'n' is even, the ends of the graph will either both rise or both fall, depending on the sign of 'a'. If 'n' is odd, one end will rise while the other falls, again determined by the sign of 'a'.
Recommended video:
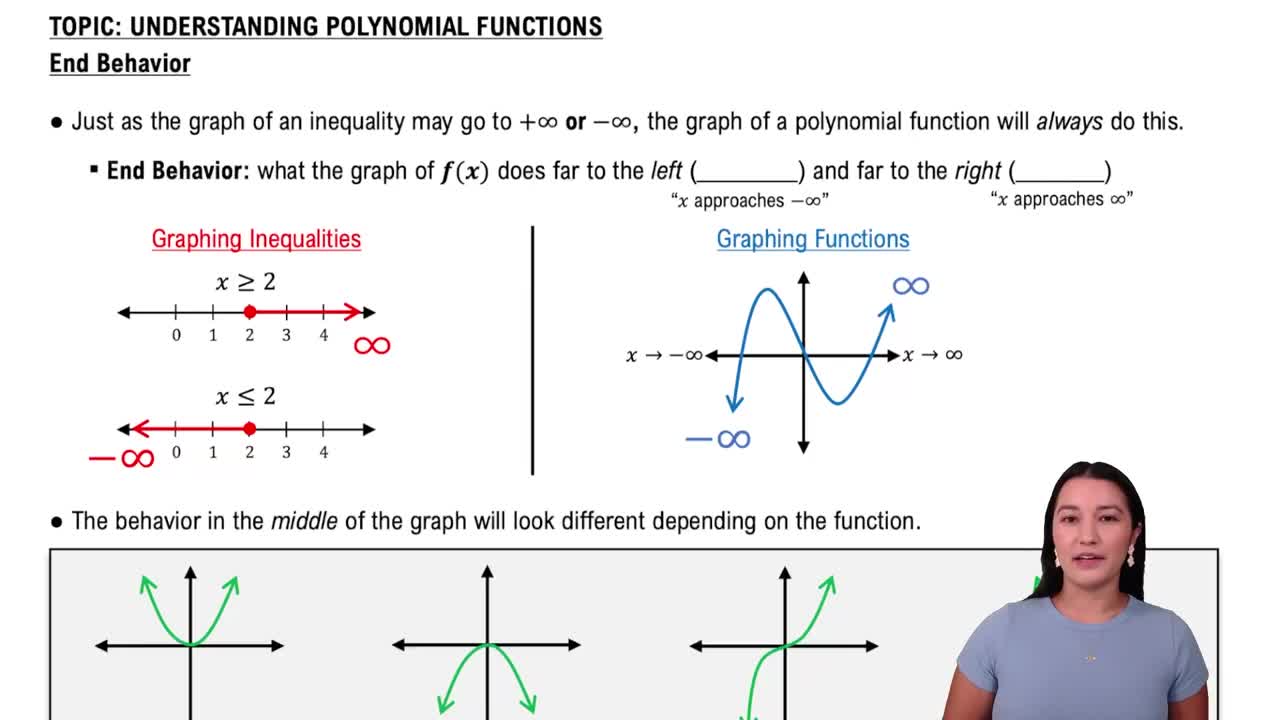
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions
Degree of a Polynomial
The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial expression. It plays a crucial role in determining the shape and end behavior of the graph. For example, a polynomial of degree 3, like f(x) = -x^3 + x^2 + 2x, will have a characteristic 'S' shape, with one end going to positive infinity and the other to negative infinity, influenced by the leading coefficient.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Standard Form of Polynomials
End Behavior of Polynomials
End behavior refers to the behavior of the graph of a polynomial function as the input values (x) approach positive or negative infinity. Understanding end behavior helps predict how the graph will behave far away from the origin. For instance, in the case of f(x) = -x^3 + x^2 + 2x, the negative leading coefficient indicates that as x approaches positive infinity, f(x) will approach negative infinity, and as x approaches negative infinity, f(x) will approach positive infinity.
Recommended video:

End Behavior of Polynomial Functions

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice