Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
Introduction to Logarithms
Problem 43
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 43– 48, match the function with its graph from choices A–F. ƒ(x) = log↓2 x
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Logarithmic Functions
Logarithmic functions, such as f(x) = log₂(x), are the inverses of exponential functions. They express the power to which a base must be raised to obtain a given number. Understanding the properties of logarithms, including their domain (x > 0) and range (all real numbers), is essential for analyzing their graphs.
Recommended video:
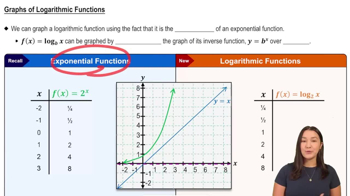
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Graphing Logarithmic Functions
The graph of a logarithmic function typically has a vertical asymptote at x = 0 and passes through the point (1, 0), since log₂(1) = 0. As x increases, the function rises slowly, reflecting the nature of logarithms growing without bound but at a decreasing rate. Familiarity with these characteristics aids in matching the function to its graph.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Transformations of Functions
Transformations of functions involve shifting, reflecting, stretching, or compressing the graph of a function. For logarithmic functions, horizontal shifts can occur when the input is adjusted (e.g., log₂(x - h)), while vertical shifts occur when a constant is added or subtracted from the function (e.g., log₂(x) + k). Recognizing these transformations is crucial for accurately interpreting and matching graphs.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions

 7:3m
7:3mWatch next
Master Logarithms Introduction with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning




