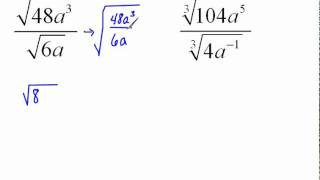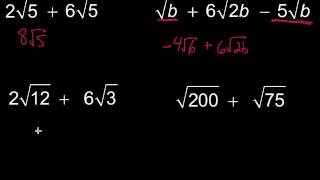Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 151
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionRationalize each denominator. Assume all variables represent nonnegative numbers and that no denominators are 0. (√7 - 1) / (2√7 + 4√2)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rationalizing the Denominator
Rationalizing the denominator involves eliminating any irrational numbers from the denominator of a fraction. This is typically achieved by multiplying both the numerator and the denominator by a suitable expression that will result in a rational number in the denominator. For example, if the denominator contains a square root, multiplying by the conjugate can help achieve this.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rationalizing Denominators
Conjugates
The conjugate of a binomial expression is formed by changing the sign between the two terms. For instance, the conjugate of (a + b) is (a - b). When multiplying a binomial by its conjugate, the result is a difference of squares, which eliminates the square roots and simplifies the expression. This technique is essential in rationalizing denominators that contain two terms.
Recommended video:

Complex Conjugates
Properties of Square Roots
Understanding the properties of square roots is crucial for manipulating expressions involving them. Key properties include that √a * √b = √(ab) and that √(a/b) = √a / √b. These properties allow for the simplification of expressions and are particularly useful when rationalizing denominators, as they help in combining and simplifying terms effectively.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Related Videos
Related Practice