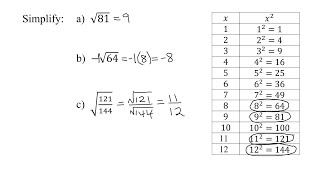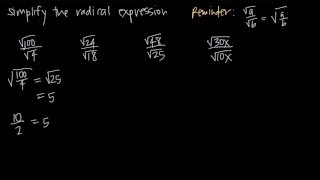Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
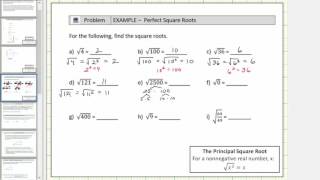
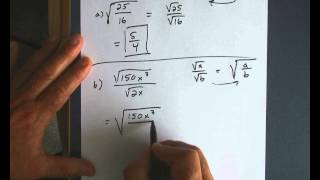
Radical Expressions
Problem 104
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 103–110, insert either <, >, or = in the shaded area to make a true statement. |−20| □ |−50|
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Absolute Value
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line, regardless of direction. It is denoted by vertical bars, such as |x|. For example, |−20| equals 20, and |−50| equals 50, as both values represent their distances from zero.
Recommended video:

Parabolas as Conic Sections Example 1
Comparing Numbers
To compare two numbers, we determine their relative sizes using symbols: < (less than), > (greater than), or = (equal to). This involves evaluating the numerical values of the two quantities. In this case, we compare the absolute values of −20 and −50 to see which is larger.
Recommended video:

The Number e
Inequalities
Inequalities express the relationship between two values that are not necessarily equal. They can indicate that one value is less than, greater than, or equal to another. Understanding how to interpret and manipulate inequalities is essential for solving problems that involve comparisons, such as the one presented.
Recommended video:

Linear Inequalities
Related Videos
Related Practice