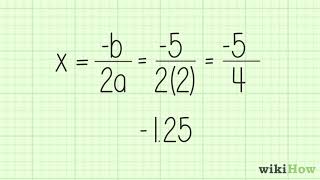Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
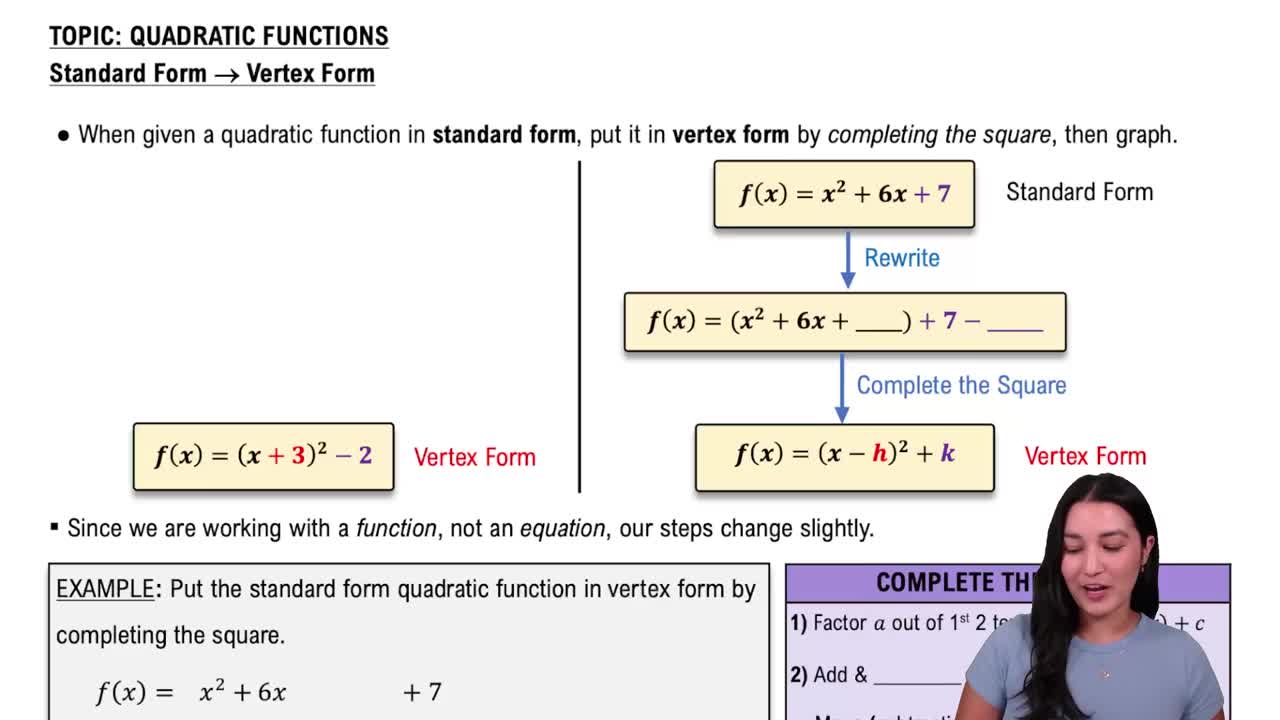
Quadratic Functions
Problem 3b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionGraph each quadratic function. Give the vertex, axis, x-intercepts, y-intercept, domain, range, and largest open intervals of the domain over which each function is increasing or decreasing. ƒ(x)=-3x^2-12x-1
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
12mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, typically expressed in the form f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, which can open upwards or downwards depending on the sign of 'a'. Understanding the general shape and properties of parabolas is essential for analyzing their characteristics.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
Vertex and Axis of Symmetry
The vertex of a quadratic function is the highest or lowest point on its graph, depending on whether the parabola opens downwards or upwards. The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that passes through the vertex, dividing the parabola into two mirror-image halves. For the function f(x) = -3x^2 - 12x - 1, the vertex can be found using the formula x = -b/(2a), which helps in determining the function's maximum or minimum value.
Recommended video:

Vertex Form
Intercepts and Intervals of Increase/Decrease
The x-intercepts of a quadratic function are the points where the graph crosses the x-axis, found by solving f(x) = 0. The y-intercept is the point where the graph crosses the y-axis, determined by evaluating f(0). Additionally, the intervals of increase and decrease can be identified by analyzing the derivative or the vertex; for a downward-opening parabola, the function decreases on the interval to the left of the vertex and increases to the right.
Recommended video:

Identifying Intervals of Unknown Behavior

 7:42m
7:42mWatch next
Master Properties of Parabolas with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice