Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
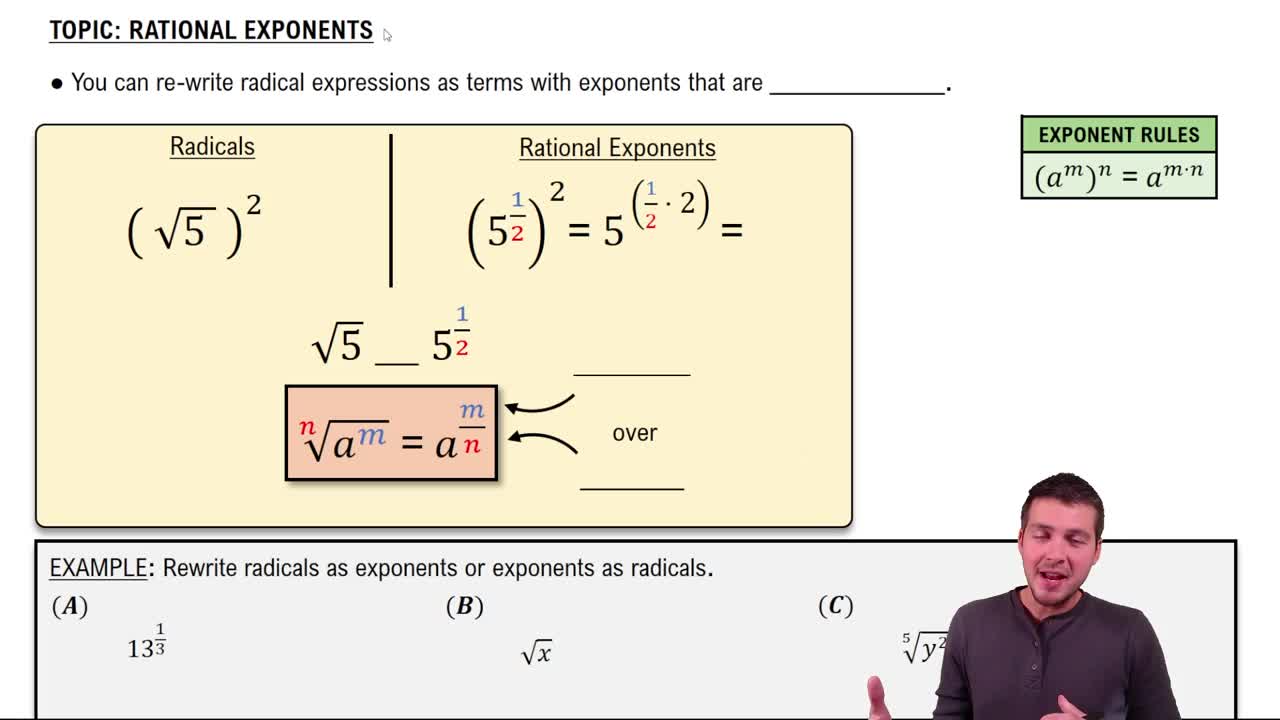
Radical Notation
Radical notation is a way to express roots of numbers using the radical symbol (√). For example, the square root of a number 'x' is written as √x. In the context of exponents, a fractional exponent indicates both a power and a root; for instance, x^(1/n) represents the nth root of x.
Recommended video:
Exponents and Fractional Exponents
Exponents are a shorthand way to express repeated multiplication of a number by itself. A fractional exponent, such as 3/2, indicates that the base should be raised to the power of 3 and then the result should be taken to the square root. This duality allows for simplification of expressions involving roots and powers.
Recommended video:
Simplification of Expressions
Simplification involves rewriting an expression in a more manageable or concise form. This can include combining like terms, reducing fractions, or applying properties of exponents and radicals. In the case of the expression 81^(3/2), simplification would involve calculating the square root of 81 and then raising the result to the third power.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Algebraic Expressions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution