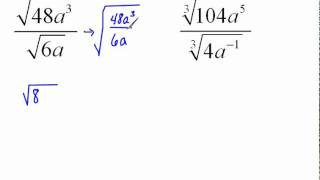Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 34e
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 33–38, express the function, f, in simplified form. Assume that x can be any real number. _______ f(x) = √81(x-2)²
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Square Root Function
The square root function, denoted as √x, is the inverse of squaring a number. It returns the non-negative value that, when squared, gives the original number. In the context of the function f(x) = √81(x-2)², understanding how to simplify square roots is essential, particularly recognizing that √(a²) = |a|, which affects the output based on the value of x.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Simplifying Expressions
Simplifying expressions involves reducing them to their most basic form while maintaining equivalence. This includes combining like terms, factoring, and applying properties of exponents and roots. In the given function, simplifying √81(x-2)² requires recognizing that 81 is a perfect square and that (x-2)² can be simplified under the square root.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Absolute Value
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line, regardless of direction, denoted as |x|. When simplifying expressions involving square roots, such as √(x-2)², it is crucial to apply the absolute value, resulting in |x-2|. This concept is vital for accurately expressing the function f(x) in its simplest form.
Recommended video:

Parabolas as Conic Sections Example 1
Related Videos
Related Practice