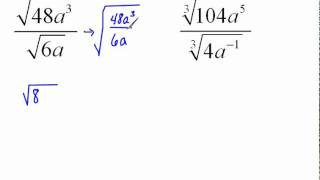Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 79a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionEvaluate each expression. See Example 7. (-4)^1/2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponents
Exponents represent repeated multiplication of a number by itself. In the expression (-4)^(1/2), the exponent 1/2 indicates the square root of the base, which is -4. Understanding how to manipulate exponents is crucial for evaluating expressions involving powers and roots.
Recommended video:
Guided course
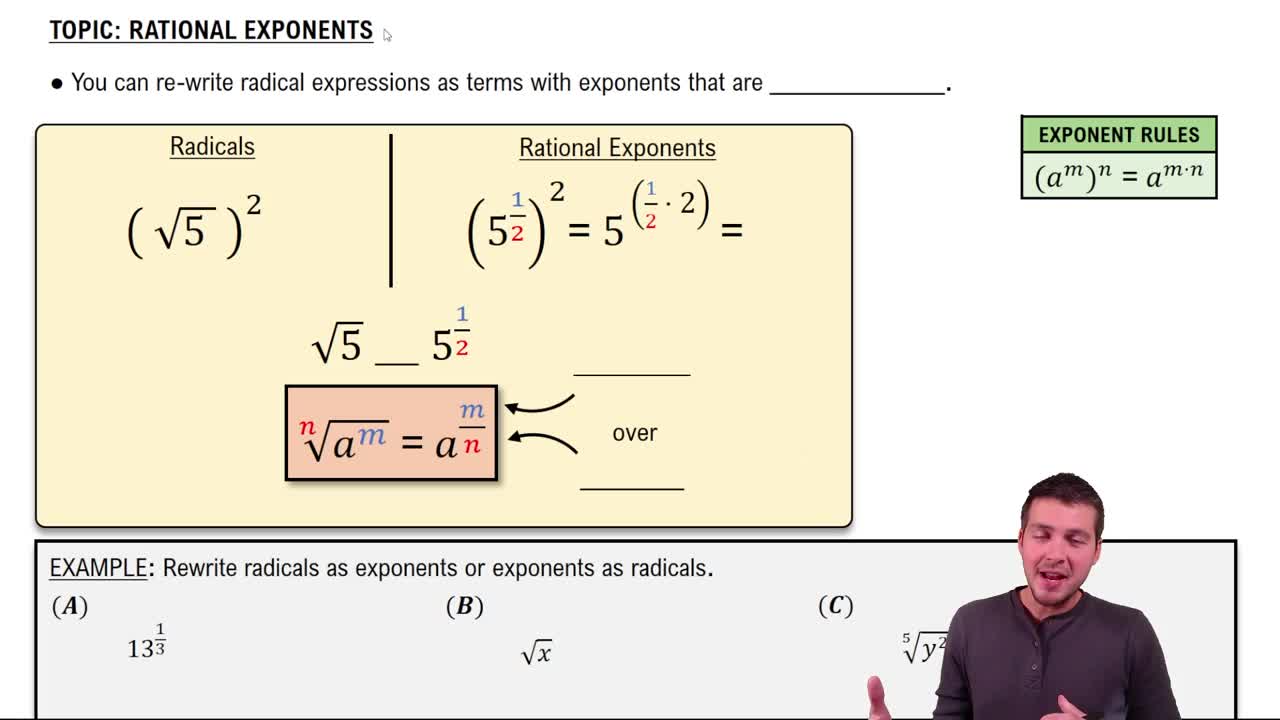
Rational Exponents
Square Roots of Negative Numbers
The square root of a negative number is not defined within the set of real numbers; instead, it leads to complex numbers. For example, the square root of -4 can be expressed as 2i, where 'i' is the imaginary unit. This concept is essential for correctly evaluating expressions that involve negative bases raised to fractional exponents.
Recommended video:

Square Roots of Negative Numbers
Complex Numbers
Complex numbers are numbers that have a real part and an imaginary part, typically expressed in the form a + bi, where 'a' is the real part and 'b' is the coefficient of the imaginary unit 'i'. Understanding complex numbers is vital when dealing with expressions that yield non-real results, such as the square root of negative numbers.
Recommended video:

Dividing Complex Numbers
Related Videos
Related Practice