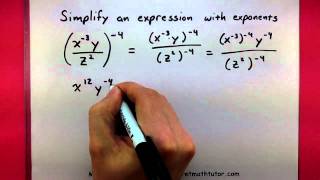Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Exponents
Problem 1a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–14, write each number in decimal notation without the use of exponents. 3.8X10²
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Scientific Notation
Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form. It is typically formatted as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and a power of ten. For example, 3.8 x 10² means 3.8 multiplied by 100, which simplifies to 380.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Decimal Notation
Decimal notation is the standard way of writing numbers using digits from 0 to 9, where the position of each digit represents a power of ten. Converting from scientific notation to decimal notation involves calculating the value of the exponent and adjusting the decimal point accordingly. This process allows for a clearer understanding of the magnitude of the number.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Exponent Rules
Exponent rules are mathematical guidelines that dictate how to handle numbers raised to a power. In the context of scientific notation, the exponent indicates how many places to move the decimal point. A positive exponent means moving the decimal to the right, while a negative exponent would mean moving it to the left, which is essential for converting to decimal notation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Exponent Rules

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice