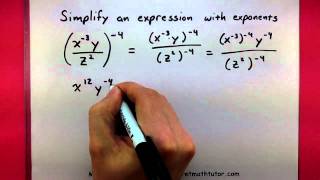Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Exponents
Problem 1a
Textbook Question
In Exercises 1–14, write each number in decimal notation without the use of exponents. 3.8X10²
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given number in scientific notation: \(3.8 \times 10^2\).
Understand that \(10^2\) means moving the decimal point 2 places to the right.
Start with the number 3.8 and move the decimal point 2 places to the right.
After moving the decimal point, fill in any empty spaces with zeros if necessary.
Write the final number in decimal notation without exponents.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Scientific Notation
Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form. It is typically formatted as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and a power of ten. For example, 3.8 x 10² means 3.8 multiplied by 100, which simplifies to 380.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Decimal Notation
Decimal notation is the standard way of writing numbers using digits from 0 to 9, where the position of each digit represents a power of ten. Converting from scientific notation to decimal notation involves calculating the value of the exponent and adjusting the decimal point accordingly. This process allows for a clearer understanding of the magnitude of the number.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Exponent Rules
Exponent rules are mathematical guidelines that dictate how to handle numbers raised to a power. In the context of scientific notation, the exponent indicates how many places to move the decimal point. A positive exponent means moving the decimal to the right, while a negative exponent would mean moving it to the left, which is essential for converting to decimal notation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Exponent Rules

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice