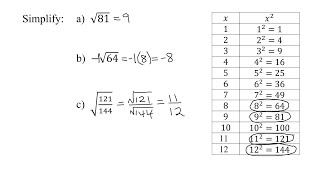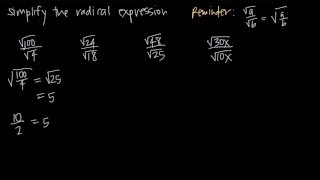Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
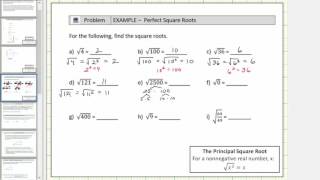
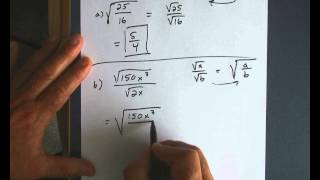
Radical Expressions
Problem 49b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 47–54, find each cube root. ___ ³√−27
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cube Roots
A cube root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, gives the original number. For example, the cube root of -27 is -3, since (-3) × (-3) × (-3) = -27. Understanding cube roots is essential for solving equations involving cubic functions and for simplifying expressions.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Negative Numbers and Odd Roots
When dealing with odd roots, such as cube roots, negative numbers have real roots. This is in contrast to even roots, where negative numbers do not yield real results. For instance, the cube root of -27 is a real number (-3), which highlights the unique properties of odd roots in algebra.
Recommended video:

Square Roots of Negative Numbers
Radical Notation
Radical notation is a way to express roots using the radical symbol (√). For cube roots, it is denoted as ³√. Understanding how to interpret and manipulate radical expressions is crucial for solving problems involving roots, as it allows for simplification and the application of algebraic rules.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Expanding Radicals
Related Videos
Related Practice