Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Transformations
Problem 13
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1-16, use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. 
g(x) = f(x/2)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Transformation
Function transformation refers to the process of altering the graph of a function through various operations, such as shifting, stretching, or compressing. In this case, the function g(x) = f(x/2) represents a horizontal stretch of the original function f(x) by a factor of 2, meaning that every x-coordinate in the graph of f(x) is doubled in g(x).
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
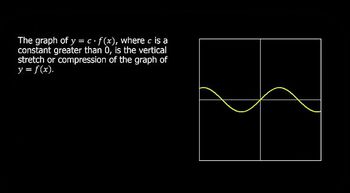
Horizontal Stretch
A horizontal stretch occurs when the x-values of a function are multiplied by a factor less than 1. For g(x) = f(x/2), the x-values are effectively halved, which stretches the graph horizontally. This transformation results in the graph of g(x) appearing wider compared to f(x), as points that were originally close together on f(x) will be spaced further apart on g(x).
Recommended video:

Stretches & Shrinks of Functions
Graph Interpretation
Graph interpretation involves analyzing the visual representation of a function to understand its behavior and characteristics. In this exercise, students must interpret the graph of f(x) to determine how the points and overall shape will change when applying the transformation to create g(x). Understanding the original graph is crucial for accurately sketching the transformed graph.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice