Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
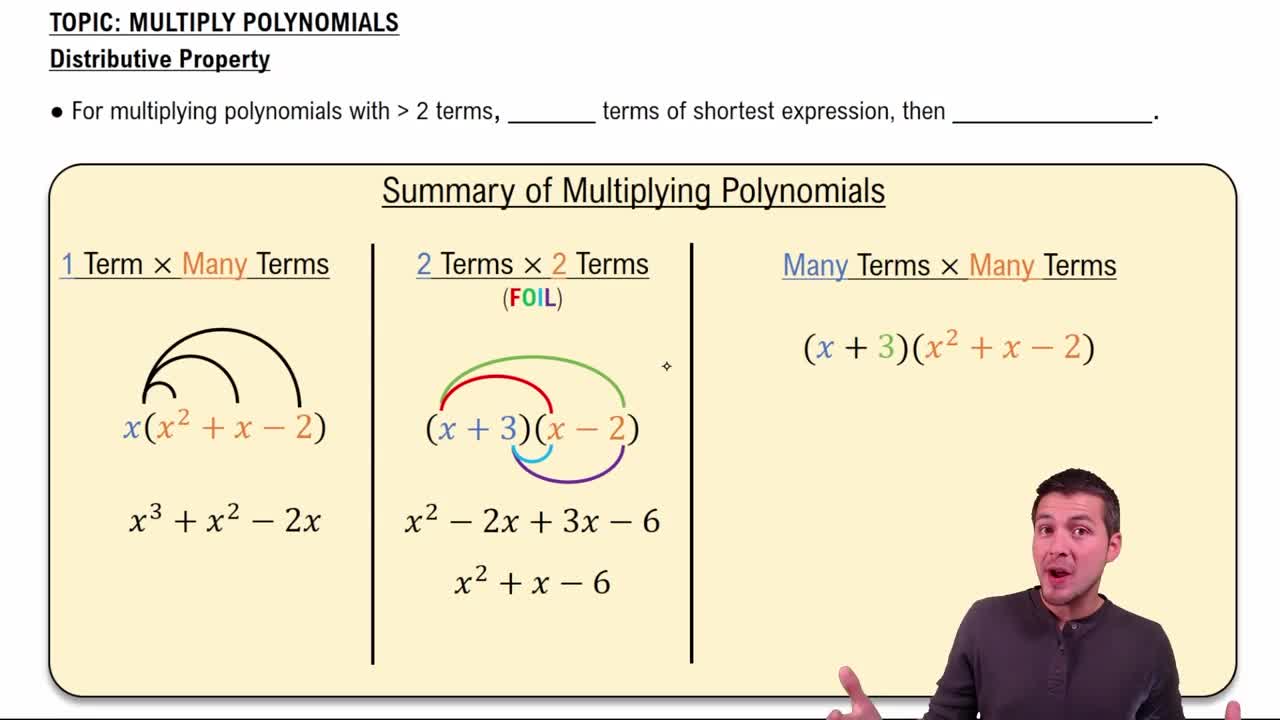
Multiplying Polynomials
Problem 1a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, multiply the monomials. (3x²)(5x⁴)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Monomials
A monomial is a polynomial with only one term, which can be a constant, a variable, or a product of constants and variables raised to non-negative integer powers. In the expression (3x²)(5x⁴), both 3x² and 5x⁴ are monomials. Understanding monomials is essential for performing operations like multiplication.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Polynomials
Multiplication of Monomials
When multiplying monomials, you multiply the coefficients (numerical parts) and add the exponents of like bases (variables). For example, in (3x²)(5x⁴), you multiply 3 and 5 to get 15, and for the variable x, you add the exponents 2 and 4 to get x^(2+4) = x⁶. This rule simplifies the multiplication process.
Recommended video:

Finding Zeros & Their Multiplicity
Exponent Rules
Exponent rules are mathematical guidelines that dictate how to handle operations involving powers. The key rule for multiplication states that when multiplying like bases, you add the exponents. This is crucial for simplifying expressions involving variables raised to powers, as seen in the multiplication of the monomials in the question.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Exponent Rules
Related Videos
Related Practice