Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Intro to Functions & Their Graphs
Problem 11b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDetermine the intervals of the domain over which each function is continuous. See Example 1. 
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Continuity of Functions
A function is continuous at a point if the limit of the function as it approaches that point equals the function's value at that point. This means there are no breaks, jumps, or holes in the graph at that point. For a function to be continuous over an interval, it must be continuous at every point within that interval.
Recommended video:

Graphs of Common Functions
Types of Discontinuities
Discontinuities can be classified into three main types: removable, jump, and infinite. A removable discontinuity occurs when a function is not defined at a point but can be made continuous by defining it appropriately. A jump discontinuity occurs when the left-hand and right-hand limits exist but are not equal. An infinite discontinuity occurs when the function approaches infinity at a certain point.
Recommended video:
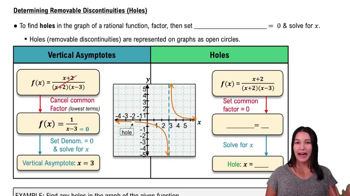
Determining Removable Discontinuities (Holes)
Interval Notation
Interval notation is a way of representing a range of values on the number line. It uses parentheses and brackets to indicate whether endpoints are included (closed interval) or excluded (open interval). For example, the interval (a, b) includes all numbers between a and b but not a and b themselves, while [a, b] includes a and b.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation

 5:2m
5:2mWatch next
Master Relations and Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice






