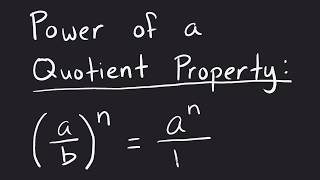
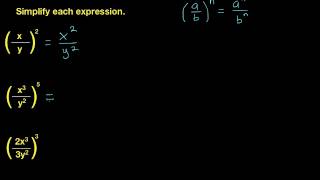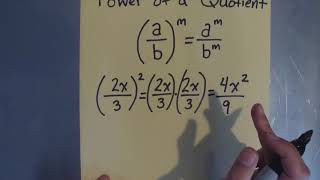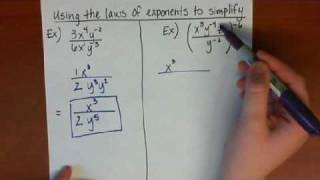Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Exponents
Problem 94a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionLet U = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13}, M = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8}, N = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13}, Q = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}, and R = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}.Use these sets to find each of the following. Identify any disjoint sets. ∅ ∩ Q
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
56sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sets and Set Notation
A set is a collection of distinct objects, considered as an object in its own right. Set notation is used to define and describe these collections, using curly braces to list elements. For example, the set M = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8} contains even numbers from 0 to 8. Understanding how to read and interpret set notation is crucial for solving problems involving sets.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Intersection of Sets
The intersection of two sets, denoted as A ∩ B, is the set of elements that are common to both A and B. For instance, if A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {2, 3, 4}, then A ∩ B = {2, 3}. This concept is essential for determining shared elements between sets, which is a key part of the question.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Parallel & Perpendicular Lines
Disjoint Sets
Disjoint sets are sets that have no elements in common, meaning their intersection is the empty set (∅). For example, if A = {1, 2} and B = {3, 4}, then A and B are disjoint because A ∩ B = ∅. Identifying disjoint sets is important for understanding relationships between different sets in the context of the problem.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice