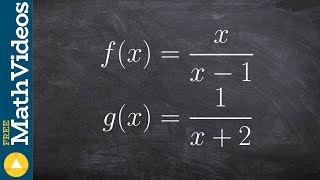Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
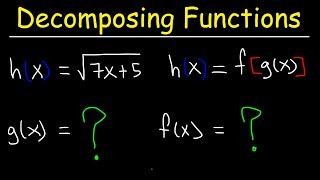
Function Composition
Problem 87b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionUse the graphs of f and g to solve Exercises 83–90. 
Find the domain of ƒ + g.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For functions f and g, the domain is determined by the x-values for which both functions yield valid outputs. Understanding the domain is crucial for operations like addition, as the resulting function ƒ + g can only be evaluated where both f and g are defined.
Recommended video:

Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Addition of Functions
The addition of two functions, denoted as (f + g)(x), involves combining their outputs for each input x. This means that for any x in the domain of both functions, (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x). To find the domain of the sum, one must identify the intersection of the domains of f and g, ensuring that both functions are defined at those x-values.
Recommended video:

Adding & Subtracting Functions Example 1
Graph Interpretation
Interpreting the graphs of functions f and g is essential for understanding their behavior and determining their domains. The graph visually represents the values of the functions, allowing one to see where they are defined (i.e., where the graph exists) and where they are not. By analyzing the points on the graph, one can easily identify the x-values that belong to the domain of ƒ + g.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Graphs and Coordinates - Example

 4:56m
4:56mWatch next
Master Function Composition with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice