Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Introduction to Rational Functions
Problem 35
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 21–36, find the vertical asymptotes, if any, and the values of x corresponding to holes, if any, of the graph of each rational function. r(x)=(x^2+4x−21)/(x+7)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. In the given function r(x) = (x^2 + 4x - 21) / (x + 7), the numerator and denominator are both polynomials. Understanding the structure of rational functions is essential for analyzing their behavior, including identifying asymptotes and holes.
Recommended video:
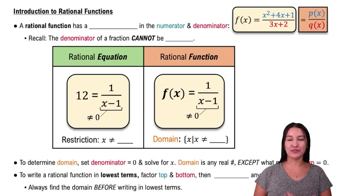
Intro to Rational Functions
Vertical Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes occur in a rational function when the denominator approaches zero while the numerator does not simultaneously approach zero. For the function r(x), we find vertical asymptotes by setting the denominator (x + 7) equal to zero, leading to x = -7. This indicates that the function will approach infinity as x approaches -7.
Recommended video:

Determining Vertical Asymptotes
Holes in the Graph
Holes in the graph of a rational function occur at values of x where both the numerator and denominator equal zero, indicating a removable discontinuity. To find holes, we factor both the numerator and denominator and identify common factors. In r(x), if the numerator can be factored to include (x + 7), it would indicate a hole at x = -7, which must be checked against the simplified function.
Recommended video:
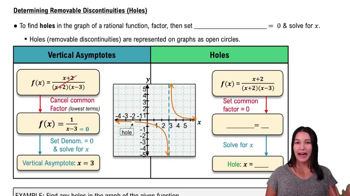
Determining Removable Discontinuities (Holes)

 6:4m
6:4mWatch next
Master Intro to Rational Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learning