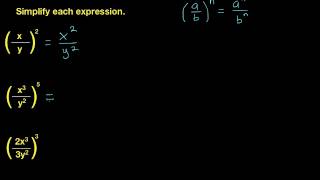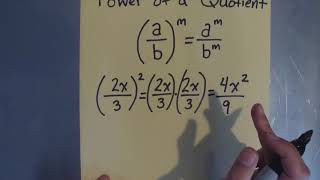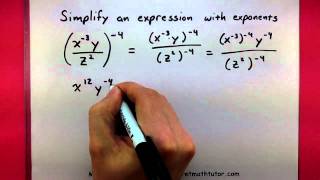Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Exponents
Problem 43d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSimplify each exponential expression in Exercises 23–64. (−3x^2 y^5)^2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponential Rules
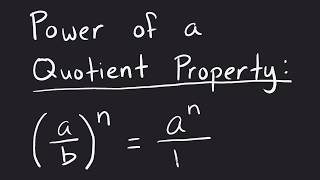
Exponential rules are fundamental principles that govern the manipulation of expressions involving exponents. Key rules include the product of powers, power of a power, and power of a product. For example, when raising a power to another power, you multiply the exponents. Understanding these rules is essential for simplifying expressions like (−3x^2 y^5)^2.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cramer's Rule - 2 Equations with 2 Unknowns
Distributive Property
The distributive property is a key algebraic principle that allows you to multiply a single term by each term within a parenthesis. In the context of exponents, this means applying the exponent to each factor inside the parentheses. For instance, in (−3x^2 y^5)^2, you would distribute the exponent 2 to −3, x^2, and y^5, leading to a simplified expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course
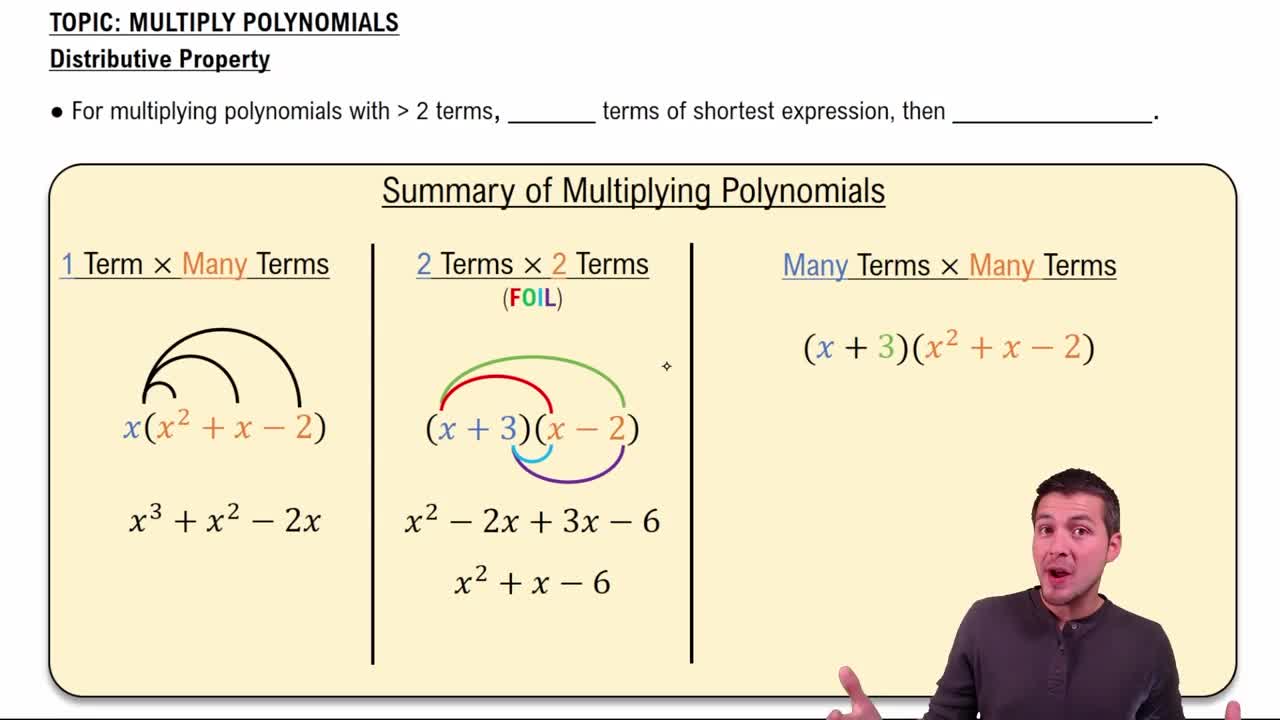
Multiply Polynomials Using the Distributive Property
Negative Exponents
Negative exponents indicate the reciprocal of the base raised to the opposite positive exponent. While this concept is not directly applicable in the given expression, understanding it is crucial for broader exponential simplifications. For example, a term like x^(-n) can be rewritten as 1/(x^n), which is important when dealing with more complex expressions involving negative bases or exponents.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Zero and Negative Rules

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice