Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, typically expressed in the form f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, which opens upwards if 'a' is positive and downwards if 'a' is negative. Understanding the basic shape and properties of quadratic functions is essential for analyzing their transformations.
Recommended video:
Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
Graph Transformations
Graph transformations involve shifting, reflecting, stretching, or compressing the graph of a function. For quadratic functions, vertical shifts occur when a constant is added or subtracted from the function, such as in g(x) = x^2 + 2, which shifts the graph of f(x) = x^2 upward by 2 units. Recognizing these transformations helps in accurately graphing modified functions.
Recommended video:
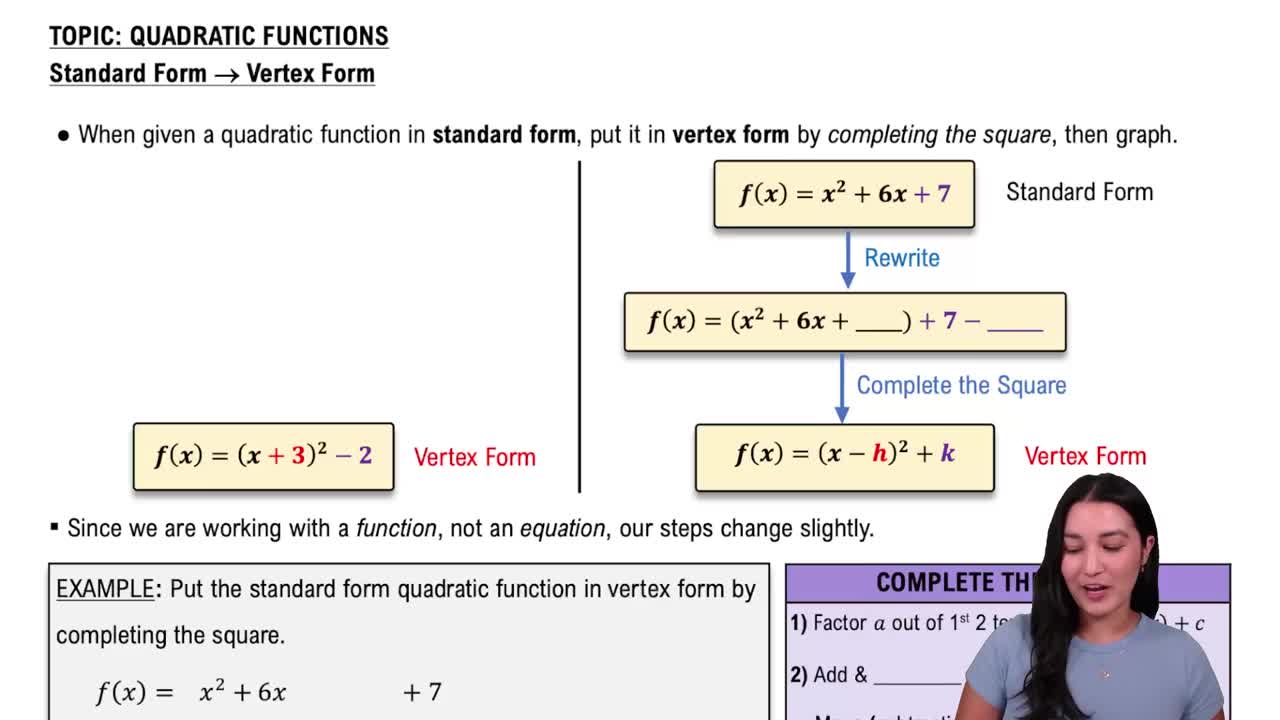
Standard Form of a Quadratic Function
The standard form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants. This form allows for easy identification of the vertex and the direction of the parabola. In the context of transformations, understanding how changes in 'c' affect the graph's position is crucial for accurately graphing functions like g(x) = x^2 + 2.
Recommended video:
Converting Standard Form to Vertex Form
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:57m
5:57m