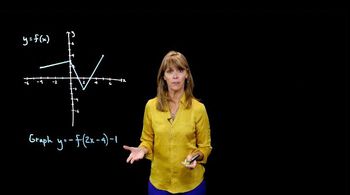Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Transformations
Problem 48
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 45-52, use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = -f(x + 1) − 1
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Transformation
Function transformation refers to the changes made to the graph of a function based on modifications to its equation. These transformations include shifts, reflections, and stretches. In the given function g(x) = -f(x + 1) - 1, the graph of f(x) undergoes a horizontal shift to the left by 1 unit, a vertical reflection across the x-axis, and a downward shift by 1 unit.
Recommended video:

Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
Horizontal Shifts
Horizontal shifts occur when the input of a function is altered, resulting in the entire graph moving left or right. In the expression f(x + 1), the graph shifts left by 1 unit because adding to the input effectively decreases the x-value needed to achieve the same output. Understanding this concept is crucial for accurately repositioning the graph of f(x) to create g(x).
Recommended video:

Shifts of Functions
Vertical Shifts and Reflections
Vertical shifts involve moving the graph of a function up or down by adding or subtracting a constant from the function's output. In g(x) = -f(x + 1) - 1, the '-1' indicates a downward shift of the graph by 1 unit. Additionally, the negative sign before f(x + 1) reflects the graph across the x-axis, inverting its values. This combination of transformations is essential for accurately graphing g(x).
Recommended video:

Graphs of Shifted & Reflected Functions

 5:25m
5:25mWatch next
Master Intro to Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice