Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Domain of a Function
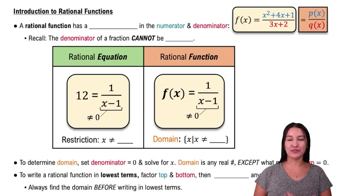
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For rational functions, the domain is typically restricted by values that would make the denominator zero, as division by zero is undefined.
Recommended video:
Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. In the case of g(x) = 2/(x+5), the numerator is a constant (2) and the denominator is a linear polynomial (x+5). Understanding the structure of rational functions is essential for determining their domains.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rational Functions
Finding Restrictions on the Domain
To find the domain of a function, one must identify any restrictions that prevent certain x-values from being included. For g(x) = 2/(x+5), the restriction occurs when the denominator equals zero, leading to the equation x + 5 = 0, which must be solved to find the excluded value.
Recommended video:
Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 4:56m
4:56m