Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
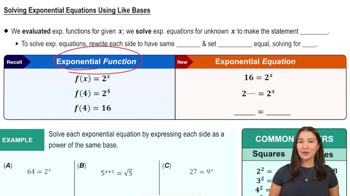
Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
Problem 73b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSolve each logarithmic equation in Exercises 49–92. Be sure to reject any value of x that is not in the domain of the original logarithmic expressions. Give the exact answer. Then, where necessary, use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. 2 log3(x+4)=log3 9+2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Logarithmic Functions
Logarithmic functions are the inverses of exponential functions and are defined for positive real numbers. The logarithm log_b(a) answers the question: 'To what power must the base b be raised to obtain a?' Understanding the properties of logarithms, such as the product, quotient, and power rules, is essential for manipulating and solving logarithmic equations.
Recommended video:
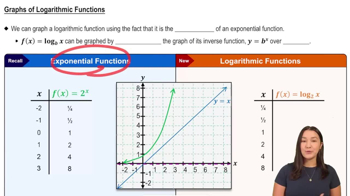
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Domain of Logarithmic Expressions
The domain of a logarithmic expression is the set of all input values (x) for which the logarithm is defined. For log_b(x), x must be greater than zero (x > 0). When solving logarithmic equations, it is crucial to check the solutions against the original expressions to ensure they fall within the valid domain, as extraneous solutions may arise during the solving process.
Recommended video:

Logarithms Introduction
Solving Logarithmic Equations
To solve logarithmic equations, one typically uses properties of logarithms to combine or simplify the expressions. This may involve rewriting the equation in exponential form or applying logarithmic identities. After finding potential solutions, it is important to verify them by substituting back into the original equation to ensure they are valid within the defined domain.
Recommended video:

Solving Logarithmic Equations

 4:46m
4:46mWatch next
Master Solving Exponential Equations Using Like Bases with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice