Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Division
Function division involves creating a new function by dividing one function by another. In this case, f/g means taking the function f(x) = 2x + 3 and dividing it by g(x) = x - 1. The resulting function, f/g, can be expressed as (2x + 3) / (x - 1), which is essential for further analysis.
Recommended video:
Multiplying & Dividing Functions
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For the function f/g, we must identify any values of x that would make the denominator g(x) = x - 1 equal to zero, as these values are excluded from the domain. In this case, x cannot equal 1, leading to the domain being all real numbers except x = 1.
Recommended video:
Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
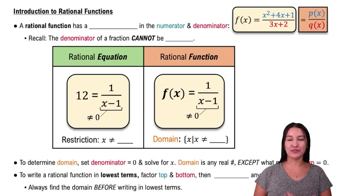
Rational Functions
Rational functions are functions that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. The function f/g is a rational function where the numerator is a linear polynomial (2x + 3) and the denominator is another linear polynomial (x - 1). Understanding the properties of rational functions, including their behavior near vertical asymptotes and discontinuities, is crucial for analyzing the function's characteristics.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rational Functions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:56m
4:56m