Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
2. Graphs of Equations
Lines
Problem 112
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWrite an equation in point-slope form and slope-intercept form of the line passing through (-10,3) and (-2,-5).
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
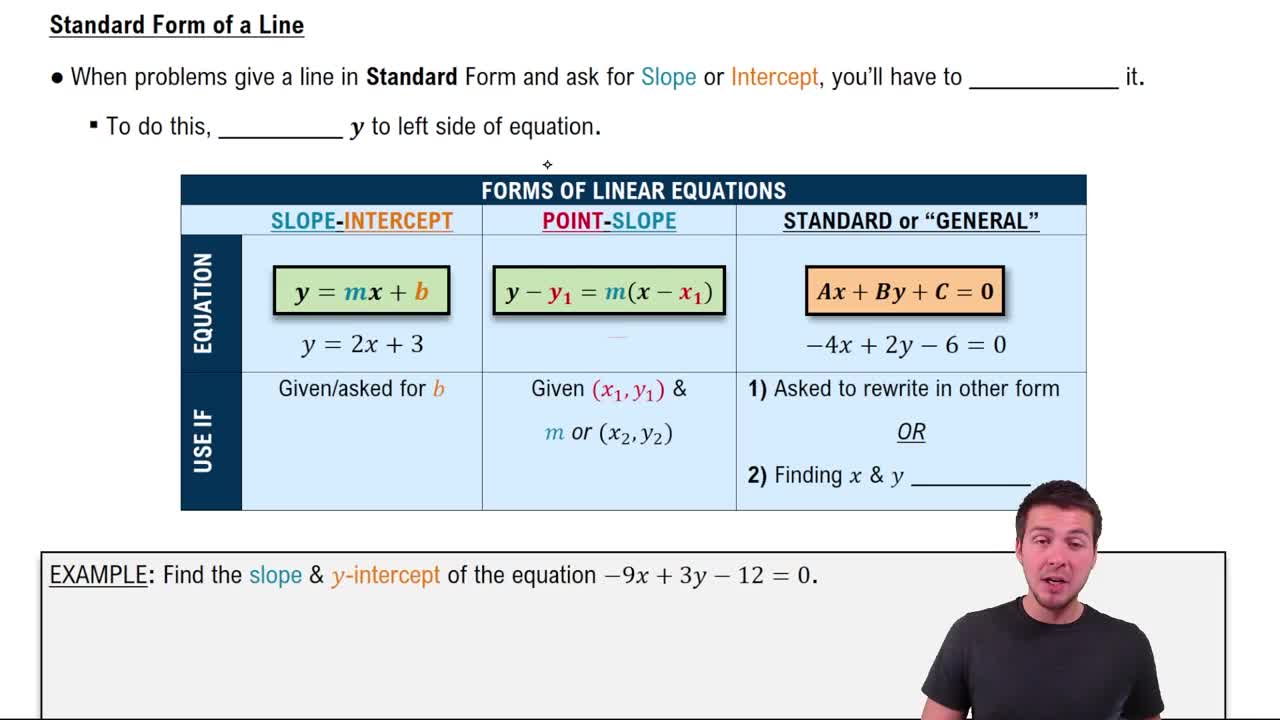
Point-Slope Form
Point-slope form of a linear equation is expressed as y - y1 = m(x - x1), where (x1, y1) is a point on the line and m is the slope. This form is particularly useful for writing the equation of a line when you know a point on the line and its slope. It allows for easy identification of the slope and a specific point, making it straightforward to graph the line.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Point-Slope Form
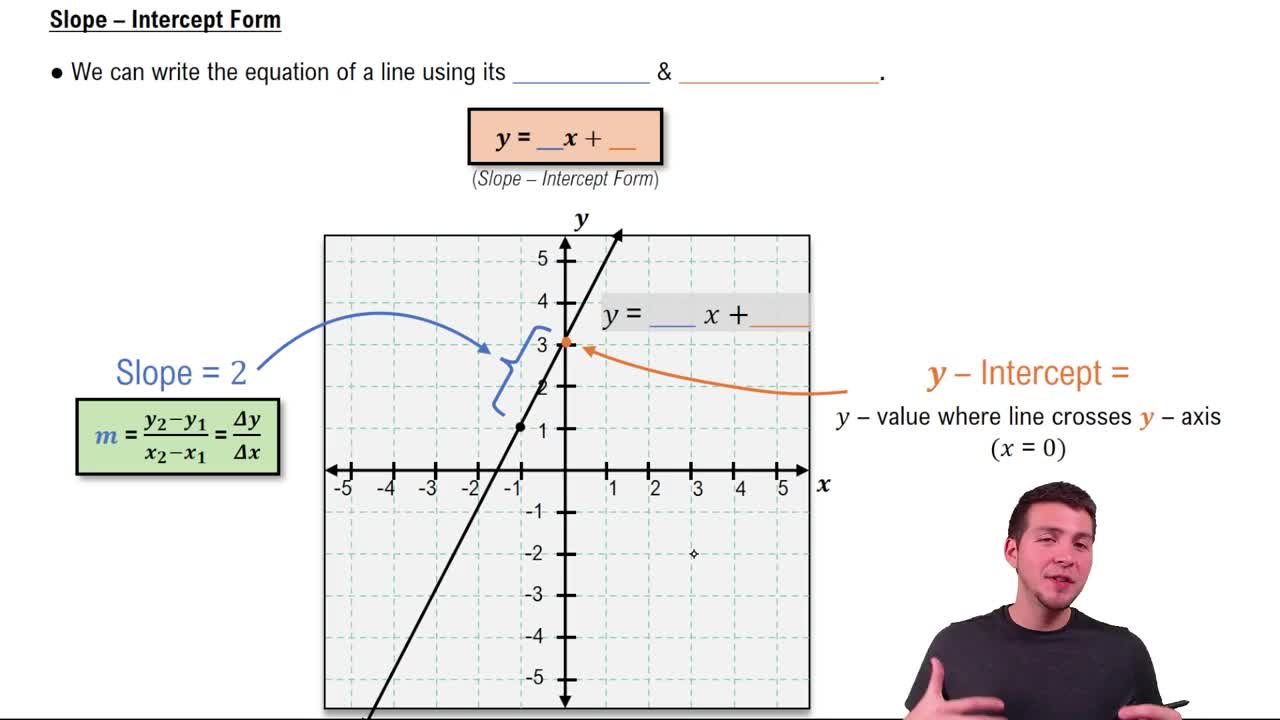
Slope-Intercept Form
Slope-intercept form is given by the equation y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept. This form is beneficial for quickly identifying the slope and where the line crosses the y-axis. Converting from point-slope to slope-intercept form can help in graphing the line and understanding its behavior in relation to the coordinate axes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Slope-Intercept Form
Calculating Slope
The slope of a line measures its steepness and direction, calculated as the change in y divided by the change in x (m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)). For the points (-10, 3) and (-2, -5), the slope indicates how much y changes for a unit change in x. Understanding how to calculate the slope is essential for both point-slope and slope-intercept forms, as it directly influences the equations derived from these points.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Slope

 6:49m
6:49mWatch next
Master The Slope of a Line with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice