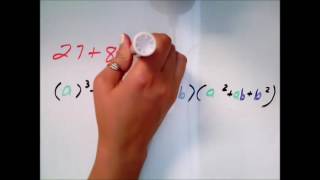Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
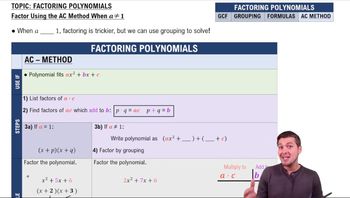
Factoring Polynomials
Problem 99d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSolve each equation in Exercises 96–102 by the method of your choice. x^3 + 2x^2 = 9x + 18
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Equations
A polynomial equation is an equation that involves a polynomial expression, which is a sum of terms consisting of variables raised to non-negative integer powers. In this case, the equation x^3 + 2x^2 - 9x - 18 = 0 is a cubic polynomial equation. Understanding how to manipulate and solve polynomial equations is essential for finding the roots or solutions of the equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Polynomials
Factoring
Factoring is the process of breaking down a polynomial into simpler components, or factors, that can be multiplied together to yield the original polynomial. This method is often used to simplify the solving process for polynomial equations. For the given equation, factoring can help identify the roots more easily, allowing for solutions to be found through setting each factor equal to zero.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Factor by Grouping
Rational Root Theorem
The Rational Root Theorem provides a way to identify possible rational roots of a polynomial equation. It states that any rational solution, expressed as a fraction p/q, must have p as a factor of the constant term and q as a factor of the leading coefficient. This theorem can guide the process of testing potential solutions for the cubic equation, helping to narrow down the candidates for roots.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Rational Exponents

 7:30m
7:30mWatch next
Master Introduction to Factoring Polynomials with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice