Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Introduction to Matrices
Problem 13a
Textbook Question
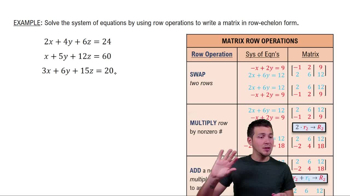
Textbook QuestionWrite the augmented matrix for each system and give its dimension. Do not solve. 2x + y + z - 3 = 0 3x - 4y + 2z + 7 = 0 x + y + z - 2 = 0
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Augmented Matrix
An augmented matrix is a matrix that represents a system of linear equations, where each row corresponds to an equation and each column corresponds to the coefficients of the variables, along with an additional column for the constants on the right side of the equations. For example, the system of equations can be transformed into a matrix format that simplifies the process of analyzing the system without solving it.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Matrices
Dimension of a Matrix
The dimension of a matrix refers to its size, expressed in terms of the number of rows and columns it contains. For an augmented matrix, the dimension is typically given as 'm x n', where 'm' is the number of equations (rows) and 'n' is the number of variables plus one (for the augmented part). Understanding the dimension helps in determining the nature of the solutions to the system.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Matrices
Linear Equations
Linear equations are mathematical statements that express a relationship between variables in which each term is either a constant or the product of a constant and a single variable. In the context of the given problem, the equations represent planes in three-dimensional space, and their intersections can provide insights into the solutions of the system. Recognizing the structure of linear equations is essential for forming the corresponding augmented matrix.
Recommended video:

Categorizing Linear Equations

 4:35m
4:35mWatch next
Master Introduction to Matrices with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice