Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Function Composition
Function composition involves combining two functions, where the output of one function becomes the input of another. In this case, fg means f(g(x)), which requires substituting g(x) into f(x). Understanding how to perform this substitution is crucial for finding the composed function.
Recommended video:
Domain of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. For rational functions like f(x) = 2 + 1/x and g(x) = 1/x, the domain excludes values that make the denominator zero, as these would result in undefined expressions.
Recommended video:
Domain Restrictions of Composed Functions
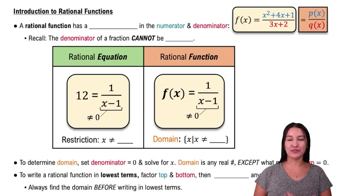
Rational Functions
Rational functions are ratios of polynomials, and they often have restrictions on their domains due to potential division by zero. In this problem, both f(x) and g(x) are rational functions, and understanding their behavior, particularly at points where the denominator is zero, is essential for determining the overall domain of the composed function fg.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rational Functions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 4:56m
4:56m