Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
4. Polynomial Functions
Understanding Polynomial Functions
Problem 55
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFor each polynomial function, identify its graph from choices A–F. ƒ(x)=(x-2)^2(x-5)^2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
8mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polynomial Functions
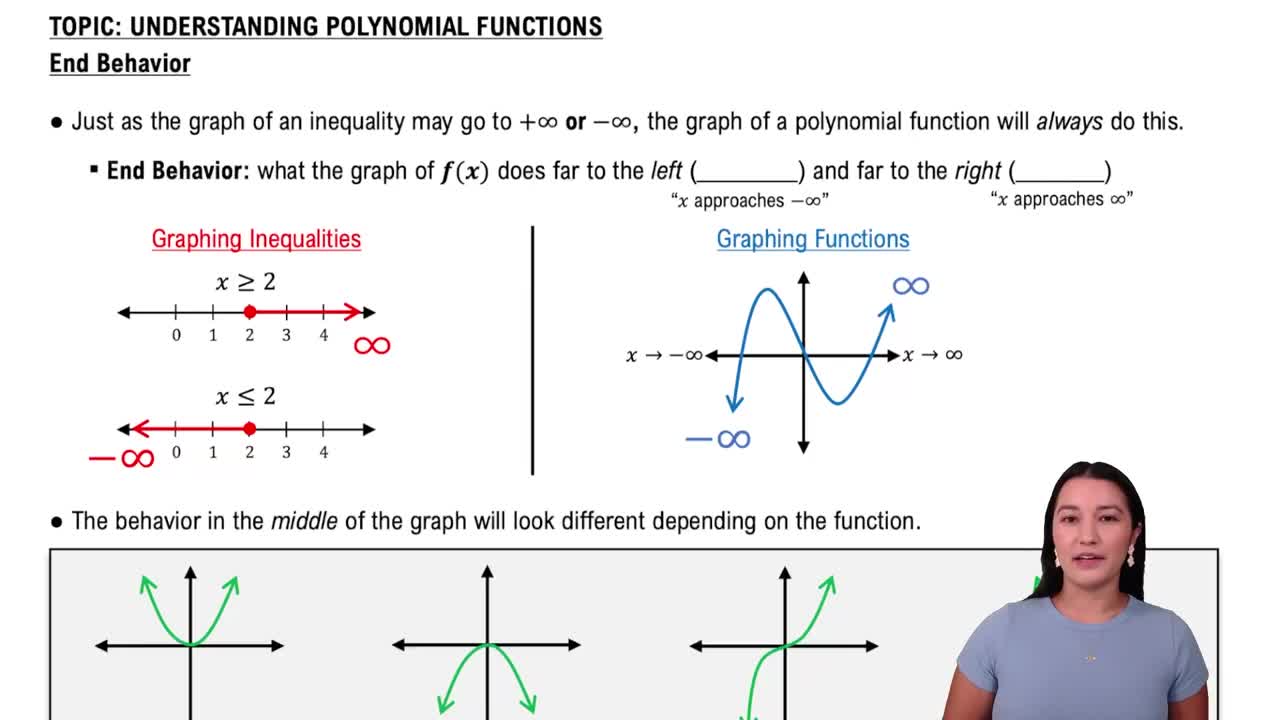
A polynomial function is a mathematical expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients. The general form is f(x) = a_n*x^n + a_(n-1)*x^(n-1) + ... + a_1*x + a_0, where n is a non-negative integer. Understanding the degree and leading coefficient of a polynomial helps predict its end behavior and the number of roots.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Polynomial Functions
Factoring and Roots
Factoring a polynomial involves expressing it as a product of its linear factors. The roots of the polynomial are the values of x that make the function equal to zero. In the given function f(x) = (x-2)^2(x-5)^2, the roots are x = 2 and x = 5, each with a multiplicity of 2, indicating that the graph touches the x-axis at these points without crossing it.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Graph Behavior and Multiplicity
The behavior of a polynomial graph at its roots is influenced by the multiplicity of those roots. If a root has an even multiplicity, the graph will touch the x-axis and turn around at that point, while an odd multiplicity means the graph will cross the x-axis. In this case, since both roots (2 and 5) have even multiplicities, the graph will touch the x-axis at these points and not cross it.
Recommended video:

Identifying Intervals of Unknown Behavior

 6:04m
6:04mWatch next
Master Introduction to Polynomial Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice