Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
1. Limits and Continuity
Continuity
Problem 16
Textbook Question
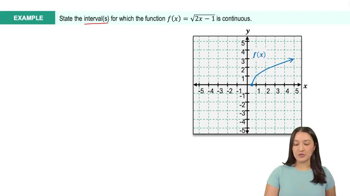
Textbook QuestionDetermine the intervals of continuity for the parking cost function c introduced at the outset of this section (see figure). Consider 0≤t≤60. <FIGURE>
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Continuity of Functions
A function is continuous at a point if the limit of the function as it approaches that point equals the function's value at that point. For a function to be continuous over an interval, it must be continuous at every point within that interval. Understanding continuity is essential for analyzing the behavior of the parking cost function over the specified range.
Recommended video:

Intro to Continuity
Intervals of Continuity
Intervals of continuity refer to the ranges of input values for which a function remains continuous. To determine these intervals, one must identify points where the function may be undefined or exhibit discontinuities, such as jumps, holes, or vertical asymptotes. This analysis helps in understanding where the parking cost function behaves predictably.
Recommended video:
Intro to Continuity Example 1
Piecewise Functions
A piecewise function is defined by different expressions based on the input value. In the context of the parking cost function, it may have different rates or rules for different time intervals. Recognizing how piecewise definitions affect continuity is crucial for accurately determining the intervals of continuity for the function.
Recommended video:
Piecewise Functions
Related Videos
Related Practice